Question
Question: The shape of \({{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\)is similar to: (A) \({{\text{C}}_{...
The shape of O2F2is similar to:
(A) C2F2
(B) O2H2
(C) H2F2
(D) C2H2
Solution
The bonding in the oxygen in dioxygen difluoride is different than the usual. This is particularly because of the very short distance between O-O the bond and a long-distance along with the O-Fbond. Thus the two O-F bonds are arranged in the two planes perpendicular to each other. Such that the O2F2 exhibit open book structure.
Complete step by step solution:
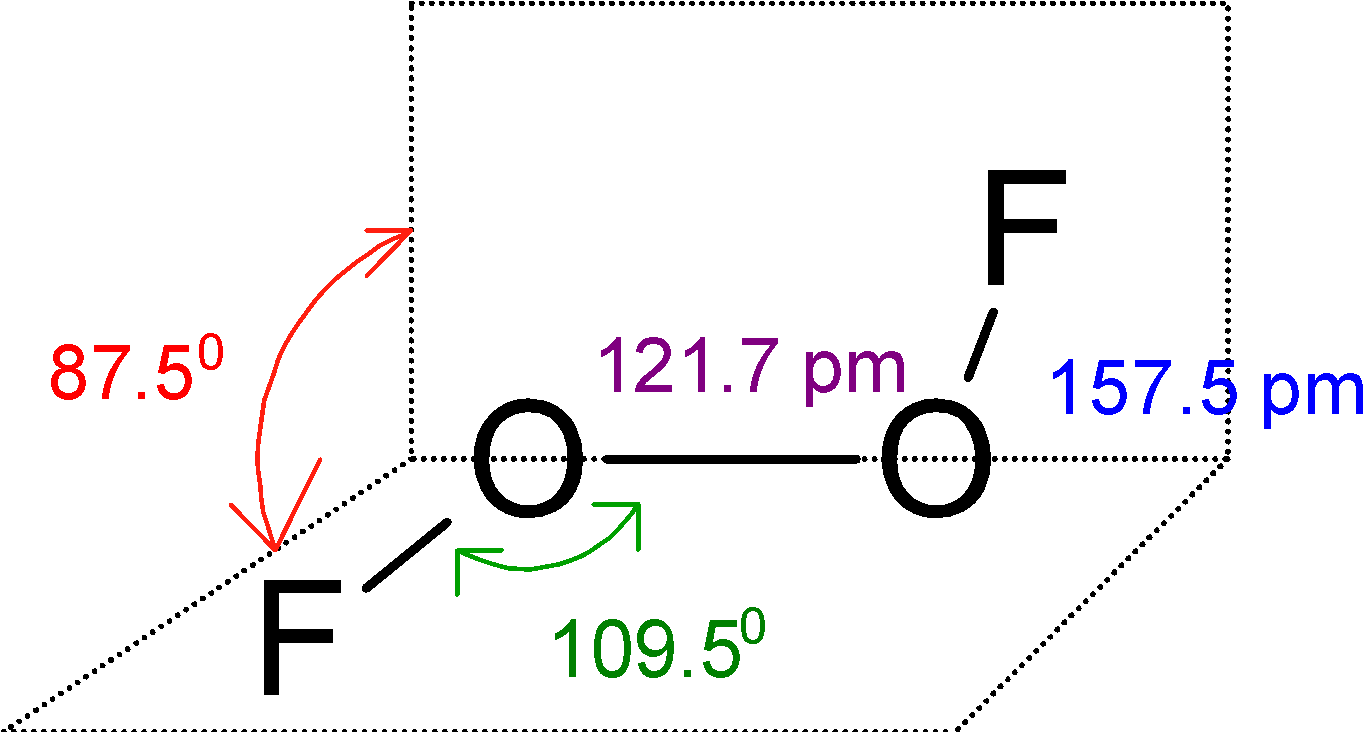
The O2F2has a large dihedral angle that approaches 900C and has C2 an axis of symmetry.
The VSEPR theory is used to decide the geometry ofO2F2.
The two oxygen atoms are bonded by the peroxide linkage. Each oxygen atom is bonded to a fluorine atom. The Lewis dot structure for the O2F2is as follows:
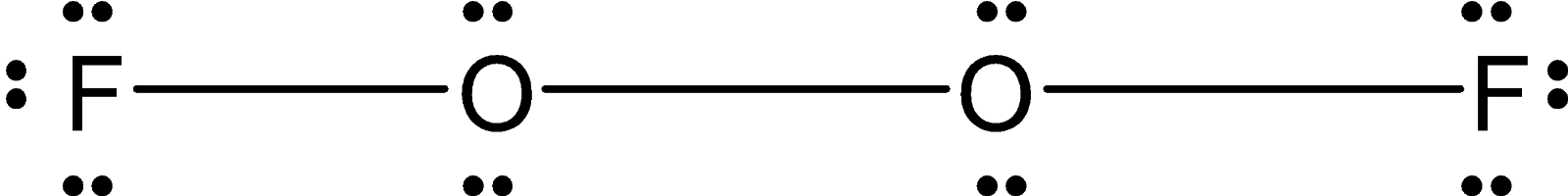
This O2F2 is an open book type structure. Since the oxygen has the two-electron pair the structure cannot be linear but it is like the fluorine atom is in a different plane. The structure is as follows:
Let's have a look at the option.
In C2F2 , the two carbon atoms are forming a covalent bond and each carbon is bonded to the two fluorine atom. the structure of the C2F2 is as shown below:
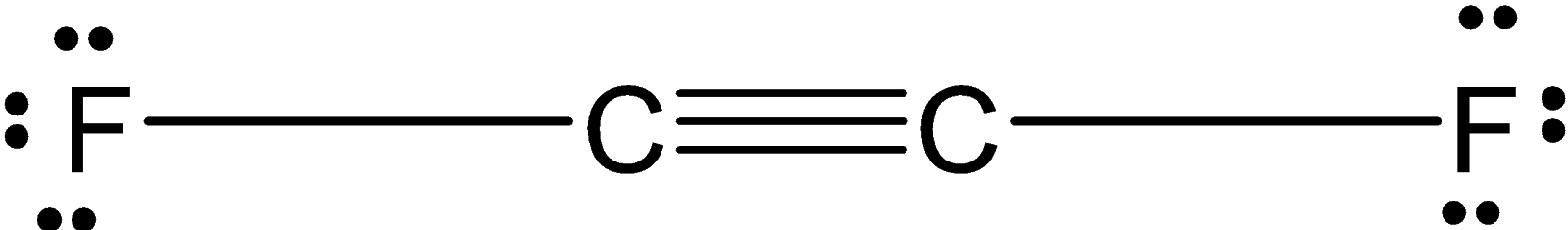
The two carbon atoms share the three bonds. Since the carbon is a sp hybridized. The C2F2 have a linear structure.
Hydrogen peroxide O2H2 is a nonplanar molecule. Two oxygen are bonded with each other forming a peroxide bond. Each oxygen atom is bonded to the hydrogen atom. Since each oxygen has two lone pairs of electrons on it. The structure is not planar. Instead of that, it is non-planar when two hydrogen atoms are in a different plane. It has an open book structure as shown below.
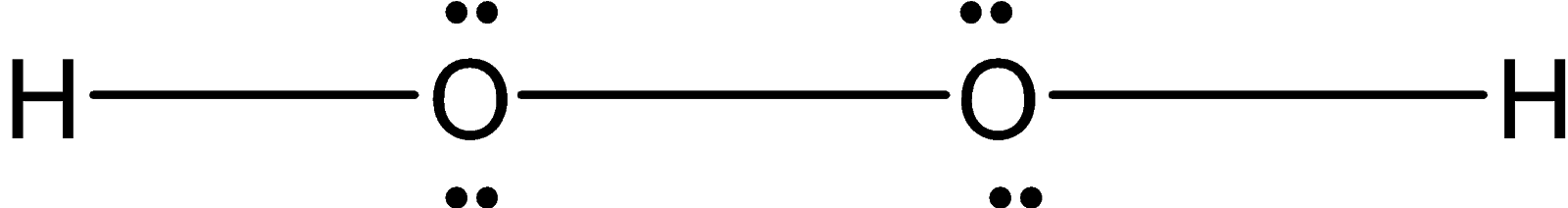
The H2F2 is a dimer of HF. Since the HF is linear molecule the dimer H2F2 is also a linear molecule.

The C2H2 is a linear molecule. Here carbon is a sp hybridized.
Therefore, hydrogen peroxide O2H2 has a similar shape O2F2.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note: In general cases, the oxygen exhibits the −2 oxidation state. The peroxides like hydrogen peroxide have an unusual oxidation state of oxygen. The compound is electrically neutral. Thus oxidation state of oxygen is:
2(+1) + 2(x) = 0+2 = −2 x∴O.S.of oxygen = −22= −1
Therefore, the oxidation state of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide is −1 .
The lone pairs on oxygen restricts the linear structure of hydrogen peroxide or O2F2 and the structure is open book structure.
