Question
Question: The shape of s -orbital____ and the shape of p- orbital....
The shape of s -orbital____ and the shape of p- orbital.
Solution
In atomic theory finding an atomic orbital is a mathematical process and quantum mechanics that describes the wave-like behaviour of one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. Every orbital can occupy a maximum of two electrons and has its own quantity of spin.
Complete answer:
There are four different orbital forms (s, p, d, and f) having different sizes, and one orbital will have a maximum of two electrons. The orbitals p, d, and f have separate sub-levels and have more electrons.
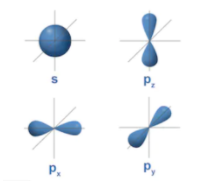
An s - orbital is spherical having nucleus in its centre and a p - orbital is dumbbell-shaped and four of the five d orbitals are cloverleaf shaped. The orbitals in an atom are found into different layers or electron shells.
The diagram for the s orbital looks like a sphere having the nucleus as its centre which is found in two dimensions and seen as a circle. So that s-orbitals are spherically symmetric having the probability of finding the electron at a given distance equal in all the directions. Increasing the value of the principal quantum number , size of the s orbital is increased.
And the shape of p-orbitals-
In we can see p- orbital consist of three lobes which lie on either side of the plane passing through the nucleus. These three p orbitals differ from the lobes are oriented whereas they are almost the same in terms of size, shape and energy. The lobes lie along one of the x, y or z-axis, and these three orbitals are given the 2px,2py,and2pz. Thus, there are three p orbitals whose axes are perpendicular. Like s orbitals, size, and energy of p orbitals will increase with increase in the principal quantum number i.e. (4p > 3p > 2p).
Hence the correct answer is (A).
Note: Where in an atom Sigma and pi bonds are formed by atomic orbital overlap. By overlapping end- to -end we find sigma bonds and Pi bonds formed when one atomic orbital lobe overlaps another.
