Question
Question: The shape of \[{\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]^{4 - }}\]ion is A.Hexagonal B.Pyra...
The shape of [Fe(CN)6]4−ion is
A.Hexagonal
B.Pyramidal
C.Octahedral
D.Octagonal
Solution
To find the shape we need to find the hybridization. To find hybridization, first draw the Lewis structure to get a rough idea about the structure of the molecule and bonding pattern. Use the valence concept to arrive at this structure. Concentrate on the electron pairs and other atoms linked directly to the concerned atom. Using the Lewis structure, calculate the number of sigma (σ) bonds and the number of lone pairs. Then calculate the steric number. Steric number is the sum of the number of σ-bonds and the number of lone pairs. Now, based on the steric number, it is possible to get the type of hybridization of the atom. Consult the following table.
| Steric number | hybridization | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | sp | Linear |
| 3 | sp2 | Trigonal planar |
| 4 | sp3 | tetrahedral |
| 5 | sp3d | Trigonal bipyramidal |
| 6 | sp3d2 | octahedral |
| 7 | sp3d3 | Pentagonal bipyramidal |
Complete answer:
Number of σ-bonds formed by the atom in a compound is equal to the number of other atoms with which it is directly linked to.
The number of lone pairs on a given atom can be calculated by using the following formula.
Number of lone pairs=2v−b−c
Where v is number of valence electrons in the concerned atom in free state (i.e., before bond formation), bis number of bonds (including both σand πbonds) formed by concerned atom and cis charge on the atom.
The Lewis structure of [Fe(CN)6]4−
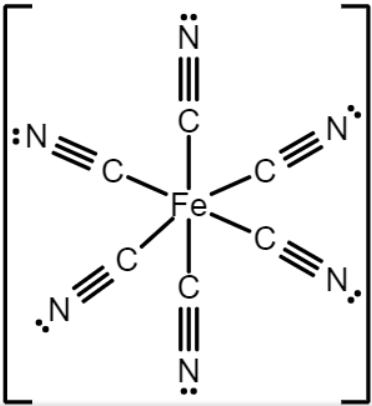
From the above structure, the central atom of iron (Fe+2) is having 6 sigma bonds and no lone pair. Which implies that the steric number of [Fe(CN)6]4−is equals to 6 and then the hybridization is sp3d.
Hence the geometry\shape of [Fe(CN)6]4− is octahedral.
Thus, the correct option is (C) Octahedral.
Note:
Planarity or nonplanarity is determined by shape/geometry which is further controlled by hybridisation of the central atom in the compound so by knowing the hybridisation we can tell whether a compound is planar or not. Hence, the molecule will not be planar if there is an sp3 hybridized carbon (or nitrogen) atom or two sp2 hybridized atoms of carbon (or nitrogen) which are separated by an even number of double bonds and no single bonds. Otherwise, its structure allows it to be planar. The polarity of a molecule is basically the measure of its dipole moment. If the dipole is a considerable number (not equal to zero), the molecule is said to be polar.
