Question
Question: The set of all points where the function \(f\left( x \right) = \sqrt {{x^2}|x|} \)is differentiable ...
The set of all points where the function f(x)=x2∣x∣is differentiable is
A.[0,∞)
B.(0,∞)
C.(−∞,∞)
D.(−∞,0)∪(0,∞)
Solution
For the given function find the domain of the function, for the values of domain plot a graph, provided that to find the set of all points where the function f(x)=x2∣x∣is differentiable, and finds the set of points with the help of the graph.
Complete step-by-step answer:
For the given function f(x)=x2∣x∣, let's find the domain of the function.
For ∣x∣=x,wherex⩾0 the function will be
⇒f(x)=x2∣x∣ ⇒f(x)=x3 ⇒f(x)=x.......(1)
So, the values of the function lie between (0,∞).
For ∣x∣=−x,wherex<0 the function will be
f(x)=x2∣x∣ ⇒f(x)=x2(−x) ⇒f(x)=−x3 ⇒f(x)=−x........(2)
So, the values of the function lie between (−∞,0).
So, the domain of the function is (−∞,0)∪(0,∞).
Plot a graph with the help of (1) and (2), i.e. y=−xandy=x
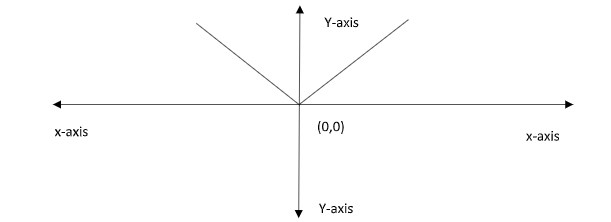
So, from the graph it is clearly indicating that the set of all points where the function f(x)=x2∣x∣ is differentiable (−∞,0)∪(0,∞).
So, option D is correct.
Note: Point to remember: When a function lies between x and y, then x and y are not included in the domain values.
