Question
Question: The sequence that correctly represents the increasing order of bond angles in \(OF_2, OCl_2, ClO_2\)...
The sequence that correctly represents the increasing order of bond angles in OF2,OCl2,ClO2 and H2O is:
A. OF2<H2O<OCl2<ClO2
B. H2O<F2O<Cl2O<ClO2
C. OF2<Cl2O<H2O<ClO2
D. ClO2<Cl2O<OF2<H2O
Solution
The bond angle in a compound is the angle formed between three atoms, with one common atom acting as the vertex, and the other two atoms bonded to it. It is directly proportional to the difference in electronegativity between the central atom and the two atoms bonded to it.
Complete step by step answer:
The bond angle is directly proportional to the difference in electronegativity between the central atom and the atoms adjacent to it, which means, the greater the difference in electronegativity, the greater the bond angle.
It can be explained simply by taking each given compound at once:
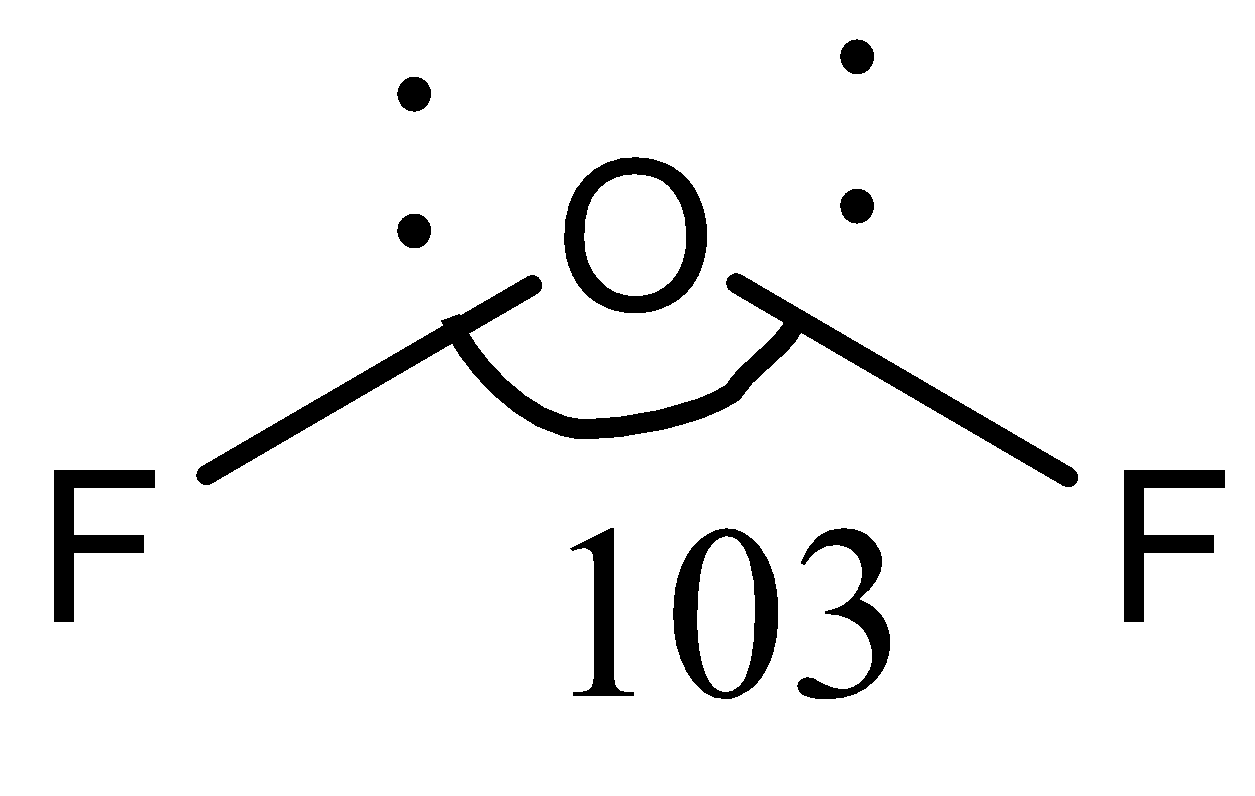
In compound OF2, the central atom is O , and the two adjacent atoms are F , written as F−O−F. As we know that fluorine is the most electronegative element in the periodic table, followed by oxygen, the difference between their electronegativities is not much. Since the difference in electronegativity is not high, the fluorine atoms are not attracted by the oxygen atom. Consequently, the electron density near the oxygen atom is also not high, and it prevents the electrons from repelling each other. This causes the fluorine atoms to be close to the oxygen atom, and the bond angle between them is small.
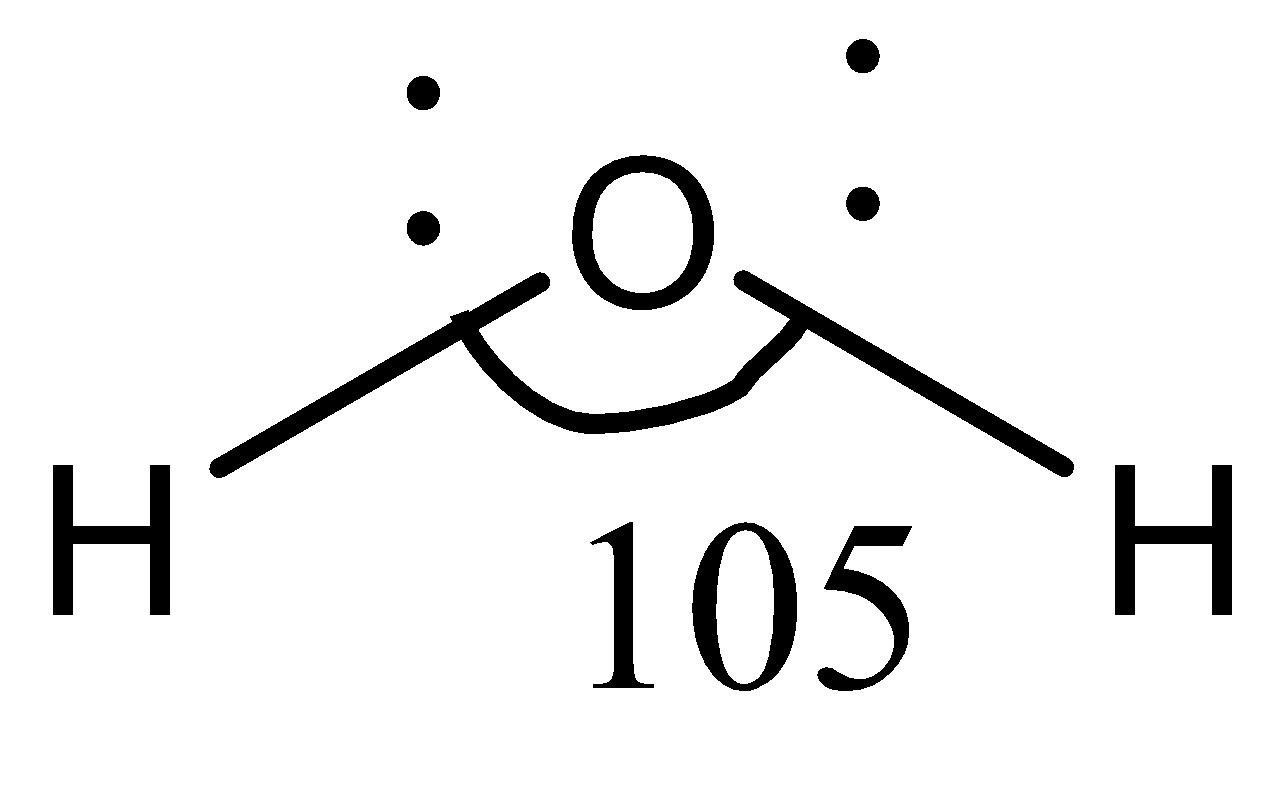
In compound H2O , the central atom, again, is O, and the two adjacent atoms are H, written as H−O−H. Hydrogen is an electropositive element, while oxygen is an electronegative element. So, the difference in their electronegativities is high, and the hydrogen atoms are pulled towards the oxygen atom. This increases the electron density near the oxygen atom, which causes the hydrogen atoms to stay afar as much as possible to gain stability. Therefore, the bond angle in H−O−H is higher as compared to OF2.
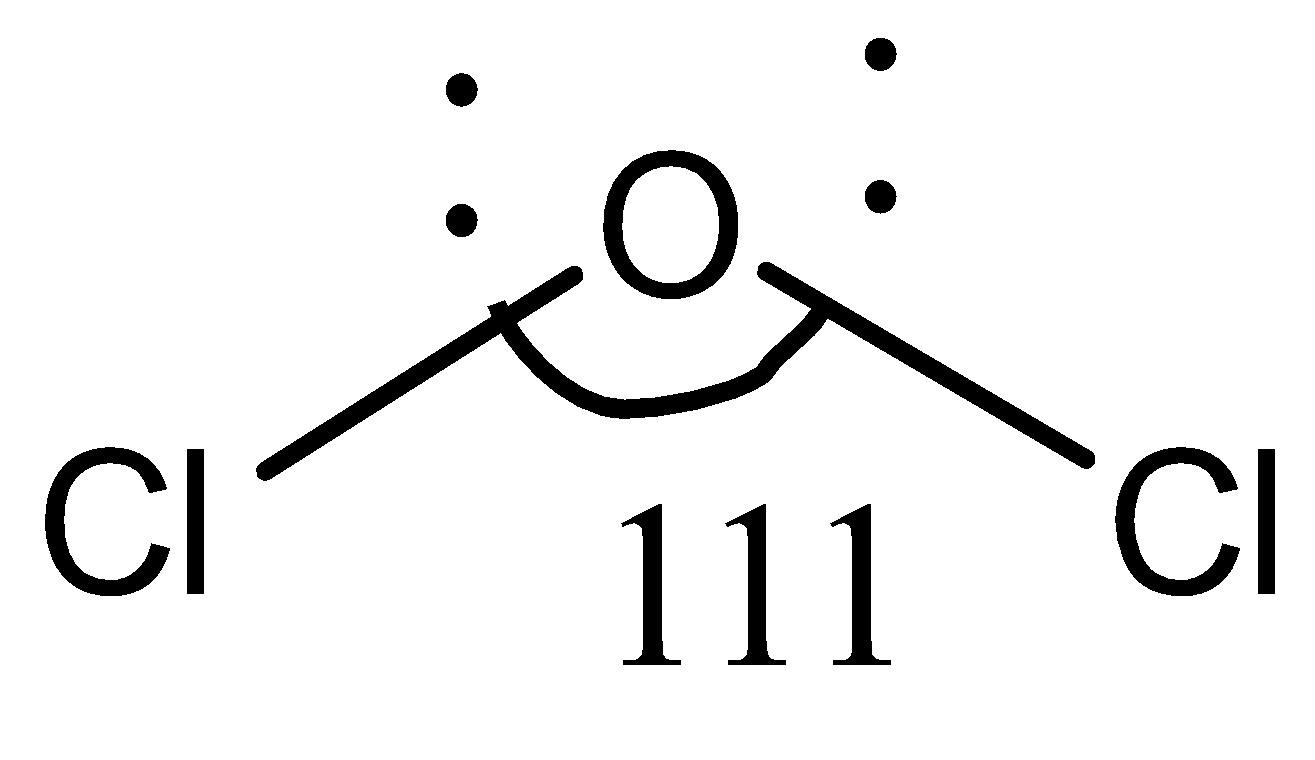
In compound Cl2O , the central atom is O , to which two chlorine atoms are bonded (Cl−O−Cl). Both chlorine and oxygen are electronegative elements, but here, the size of the chlorine atoms comes into play. The chlorine atom has a larger size. So, in Cl−O−Cl, there is steric repulsion between the two chlorine atoms, unlike in F−O−F. Due to this steric repulsion, the chlorine atoms tend to stay away from each other to minimize repulsion to their best. Therefore, the bond angle in Cl2O is greater than that in OF2 and H2O.
In compound ClO2, the central atom, Cl, is bonded to two O atoms, represented as O−Cl−O.
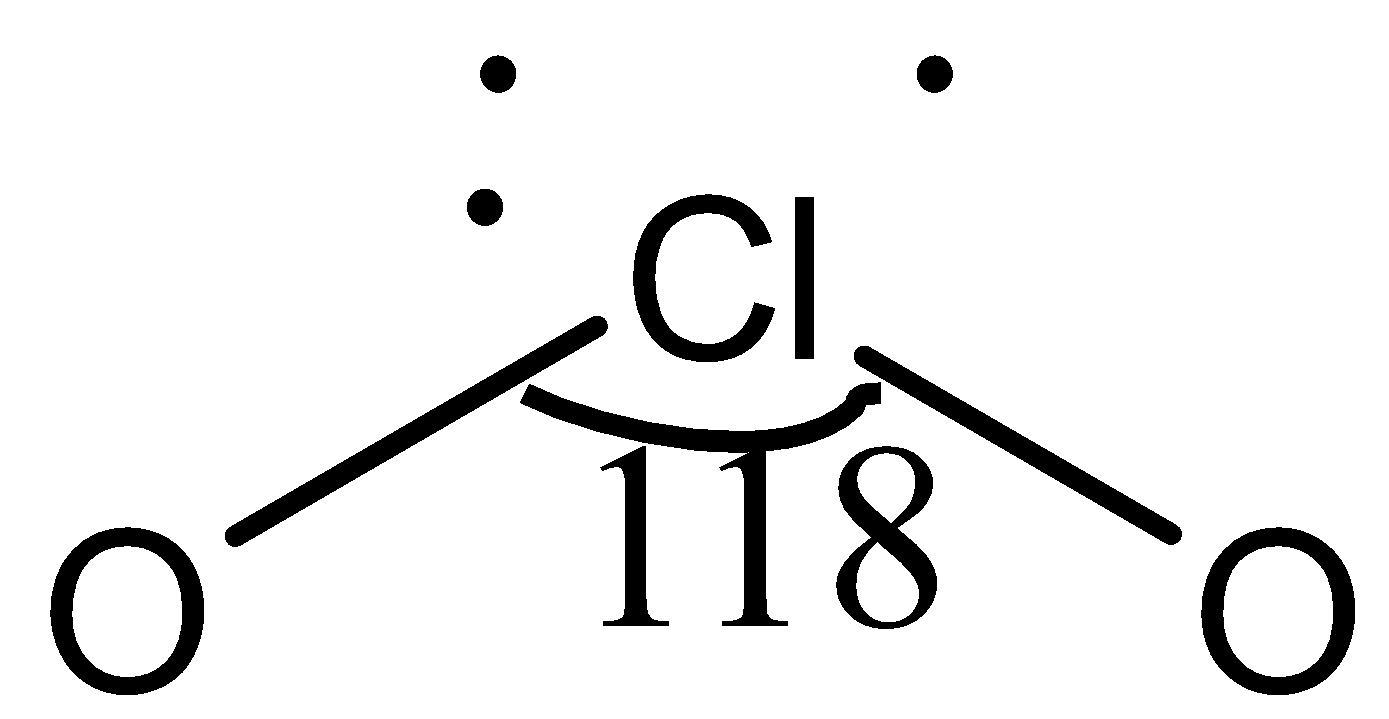
Here, there are only three lone electrons on the chlorine atom, whereas, in all other given compounds, there are four lone electrons. Due to this, a partial double bond develops between the chlorine atom and one oxygen atom, and bond pair-bond pair repulsion takes place. Due to this repulsion, the bond angle in ClO2 is maximum.
Therefore, the correct order of increasing bond angles in the compounds is:
OF2<H2O<OCl2<ClO2
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: It should be taken note that increasing order of bond angle means the order of bond angle arranged from smallest to highest.
It must be kept in mind that only the valence electrons participate in bonding, and the valence electrons which do not take part in bonding are called lone electrons.
Bond pair-bond pair repulsion is the repulsion taking place between two adjacent bonds.
