Question
Question: The reversible expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic and isothermal conditions is shown in the f...
The reversible expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic and isothermal conditions is shown in the figure. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
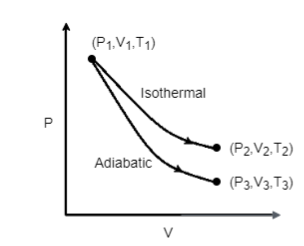
This question has multiple correct options
A.T1=T2
B. T3>T1
C. wisothermal>wadiabatic
D. ΔUisothermal>Δadiabatic
Solution
Ideal gas is defined as the gases in which collisions between the atoms are elastic and there are no intermolecular attractive forces. The ideal gas law is defined as the product of pressure and volume of a molecule is equal to the product of gas constant and temperature. Ideal gas is a hypothetical gas that tells us about the behavior of gases under many conditions.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, a graph is plotted between pressure and volume where reversible expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic and isothermal conditions is given.
Let us discuss the options one by one.
A.For an isothermal process where the temperature of the system remains constant, T1 and T2 are two temperatures plotted in an isothermal graph. And as we know the temperature is constant in the isothermal process, so T1=T2 .
Hence, the option (A) is correct.
B.In this option, T1 and T3 are the two temperatures plotted in a adiabatic graph. From the first law of thermodynamics we know that U=Q−W
where, U is the internal energy, W is the work done and Q is the heat.
Work done by the system is positive.
For adiabatic processes, Q=0 as there is no transfer of heat.
Therefore, U=−W
For an ideal gas expansion, we observed that work done by the system is positive, that means, W>0
Hence, U<0 and internal energy decreases. If internal energy decreases, then temperature also increases because internal energy is directly proportional to temperature.
Therefore, T1>T3 , so this option is incorrect.
C.For isothermal ideal gas equation, PV=constant
For adiabatic ideal gas equation, PVγ=constant
If we want to compare the PV work quantities, firstly we need to examine the slope dVdP
The work done will be greater if the area under the work is more.
For isothermal process:
(dVdP)T=−VP
For adiabatic process:
(dVdP)Q=−γVP
The γ value is always greater than one, and as we can see that there is a negative sign in both the expressions, making the value of work done for isothermal process greater than work done by adiabatic process.
Hence, we can say that wisothermal>wadiabatic
So, this option is correct.
D.For isothermal processes, the internal energy is constant because internal energy is a function of temperature.
U=constant
⇒ΔU=0
For adiabatic process, as we know that Q=0
ΔU=ΔQ−ΔW
Therefore, ΔU=−W
Hence, we can say that ΔUisothermal>ΔUadiabatic
So, this option is also correct.
Therefore, the correct options are (A), (C) and (D).
Additional information:
-Ideal gas law is the hypothetical equation of ideal gas. It tells us about the behavior of gases under many conditions. This law does not tell us about whether the gas heat or cools during expansion and compression.
-Adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which there is no transfer of heat. Adiabatic process is also known as isentropic process. In this process, work transfer of the system is frictionless, no transfer of heat and the process is reversible.
-Ideal gases are the point masses that move in random straight-line motion.
-Ideal gas law is the combination of simple gas law that is Boyle’s law, Charles law and Avogadro’s law.
-One pascal cubic meter is equal to the one joule.
-Isothermal process is defined as a thermodynamic process where temperature of the system remains constant. The thermal equilibrium is maintained because transfer of heat occurs very slowly. Some examples of isothermal processes are refrigerator, heat pumps.
Note: Adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process where there is no transfer of heat.
-It is denoted with a symbol ′Q′. For this process, Q=0 .
-If work is done on the system, then work done is positive and if work is done by the system, then work done is negative. The work done in terms of pressure and volume is done by frictionless piston and ideal gases.
