Question
Question: The resistance of an ammeter is \[13\Omega \] and its scale is graduated for a current upto \(100A\)...
The resistance of an ammeter is 13Ω and its scale is graduated for a current upto 100A . After an additional shunt has been connected to this ammeter it becomes possible to measure currents up to 750A by this meter. The value of shunt-resistance is-
A. 2KΩ
B. 20Ω
C. 2Ω
D. 0.2Ω
Solution
In this question, we need to determine the value of shunt-resistance such that it has been connected to increase the current reading of the meter. For this, we will use the concept of flow of current across the parallel connected resistances and the formula for shunt resistance of an ammeter.
Complete step by step solution:
Here the resistance is called shunt resistance. Shunt resistance needs to be connected in parallel to the galvanometer. But here an ammeter is already given whose range is to be increased. We can use the same concepts of a galvanometer conversion to ammeter by treating the ammeter as the galvanometer and the resistance of ammeter as the resistance of the galvanometer.
The formula for shunt resistance is given by S=I−igigG
Here G is the resistance of the ammeter, I is the previous range of the ammeter and ig is the new range of the ammeter.
The appropriate arrangement of the components are done as
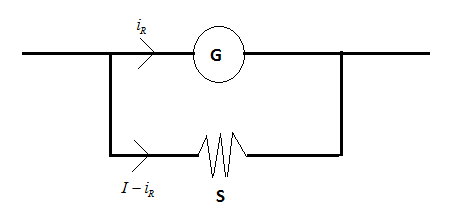
Given in the question,
G=13Ω I=750A ig=100A
We put the values of these in the equation of shunt resistance
S=750−10013×100 ⟹S=6501300 ⟹S=2Ω
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Using this formula and the apparatus we can convert a galvanometer into an ammeter.
Also by using the same arrangement we can even increase the range of an existing ammeter which is done in question. We can use the same concepts of a galvanometer conversion to ammeter by treating the ammeter as the galvanometer.
