Question
Question: The reagent \(\left[ X \right]\) is? 
Solution
This question gives the knowledge about the carbylamine reaction. This reaction is also called as Hoffman’s isocyanide test which is responsible for the detection of primary aliphatic and aromatic amines.
Complete step by step answer:
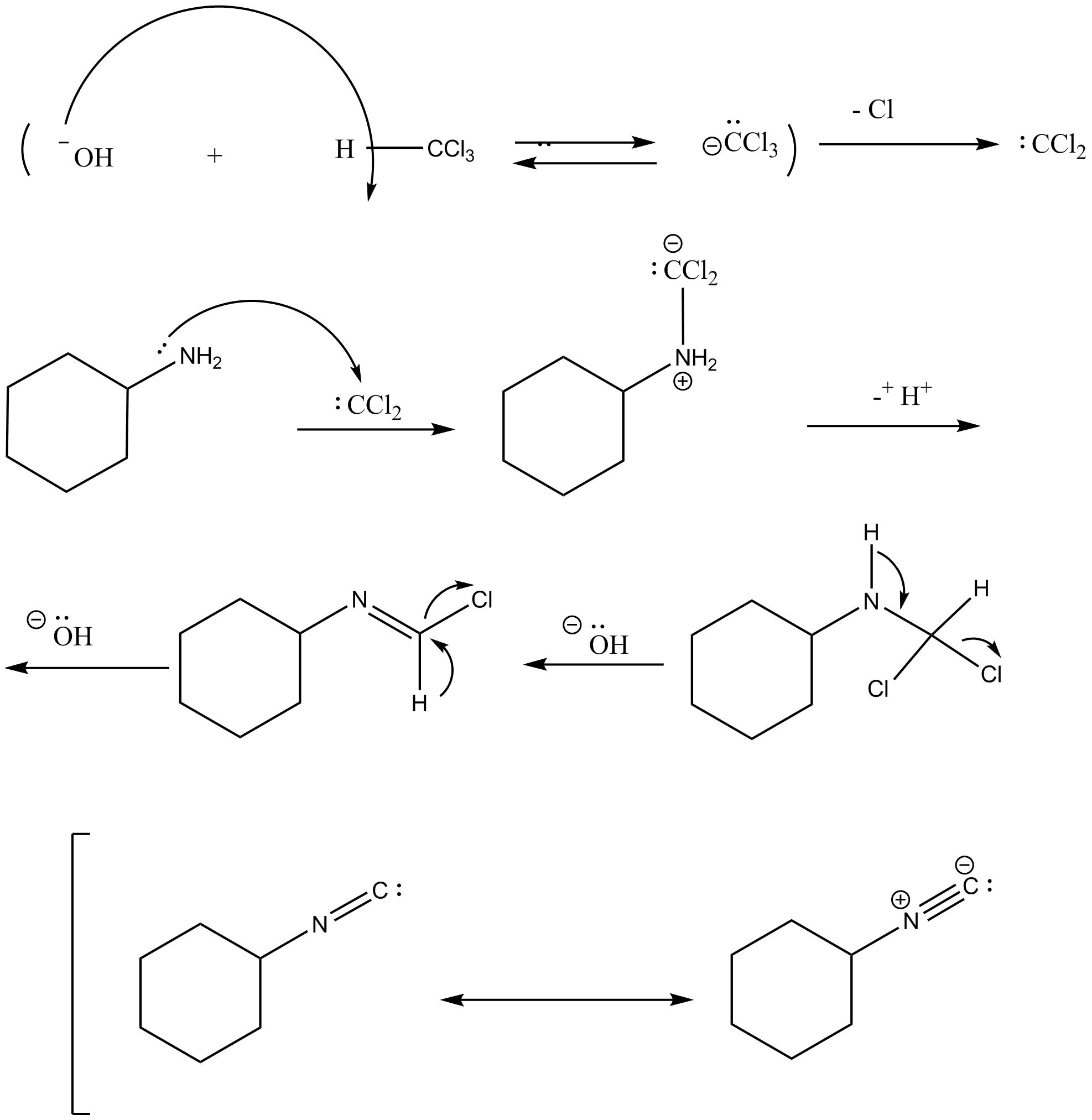
Carbylamine reaction is also called as Hoffman’s isocyanide test which is responsible for the detection of primary aliphatic and aromatic amines. This reaction involves the formation of carbene intermediate. Secondary amines and tertiary amines do not give positive Hoffman’s isocyanide test. Isonitrile is also known as isocyanide. Isocyanide is a chemical compound having functional group (−C≡N). This reaction involves the formation of carbene intermediate which is a short lived neutral species. Carbenes are of two types, which are singlet carbene and triplet carbene.
Mechanism of the carbylamine reaction is as follows:
In the first step, dehydrohalogenation of chloroform takes place in which hydroxide ion reacts with chloroform and abstracts the hydrogen and removes the chloride ion and leads to the formation of carbene intermediate namely dichlorocarbene. The dichlorocarbene is highly reactive in nature.
In the next step, dichlorocarbene reacts with amine followed by two consecutive base catalyzed dehydrochlorination steps which leads to the formation of isocyanide. In this step, dichlorocarbene is an electrophile and amine is a nucleophile.
In the next step, removal of hydrochloric acid takes place and leads to the formation of isonitrile which is also known as isocyanide.
Note: Always remember the mechanism of carbylamine reaction. And also remember how the formation of carbene intermediate takes place. Hoffman’s isocyanide test is responsible for the detection of primary aliphatic and aromatic amines.
