Question
Question: The reagent (C) in the following chemical reaction is:  in the following chemical reaction is:
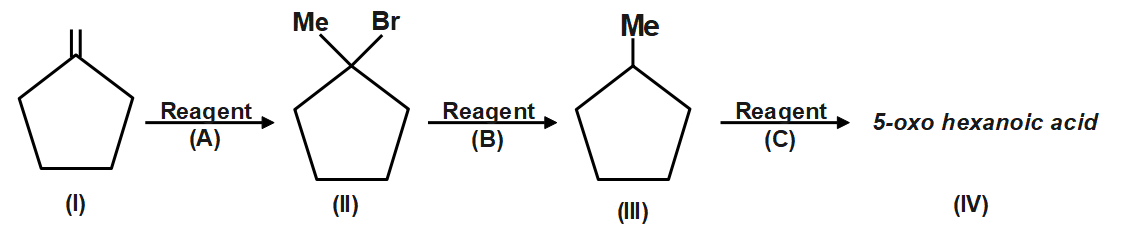
(A) O3/Ph3P
(B) O3/NaBH4
(C) O3/H2O2
(D) KMnO4/O⊕H
Solution
Hint : We know that an oxidizing agent is an acceptor of electrons also, an oxidizing agent can be seen as a species capable of transferring electronegative atoms (especially oxygen) to a substrate. Sometimes classified as oxidants or oxidizing agents.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Ozone is an oxidizing agent: Ozone serves as a strong oxidizing agent as an atom of nascent oxygen that is more reactive than oxygen will quickly decompose to give. A strong oxidizing agent absorbs and reduces electrons, and is usually described by halogens or an oxygen-consisting product. It will hand it out to another material readily. The state of oxidation of these substances is decreasing. Ozone decomposes to liberate nascent oxygen atoms.
Ozone is a reducing agent: Ozone converts peroxides to oxides, and is converted to oxygen in exchange. Hydrogen peroxide is reduced to hydrogen by ozone. Since an acid (5-Oxohexanoic acid) is obtained, so is oxidative ozonolysis. Reagent (C) will give this product.
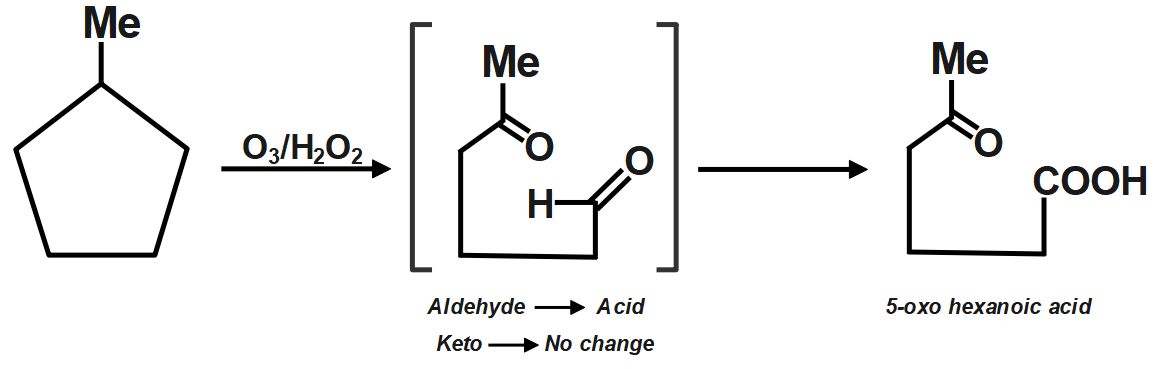
Additional Information:
Ozone (O3) is a highly reactive gas that consists of three oxygen atoms. This is both a natural and a man-made product which occurs in the upper molecule of ozone (the stratosphere) and lower atmosphere (the troposphere) of the Earth. Ozone impacts life on Earth in either good or negative ways, depending upon where it is in the atmosphere.
Note :
Note that an oxidizing agent is a reactant that removes electrons during a redox reaction from other reactors. Usually, the oxidizing agent takes those electrons for itself, thus obtaining electrons and reducing them.
