Question
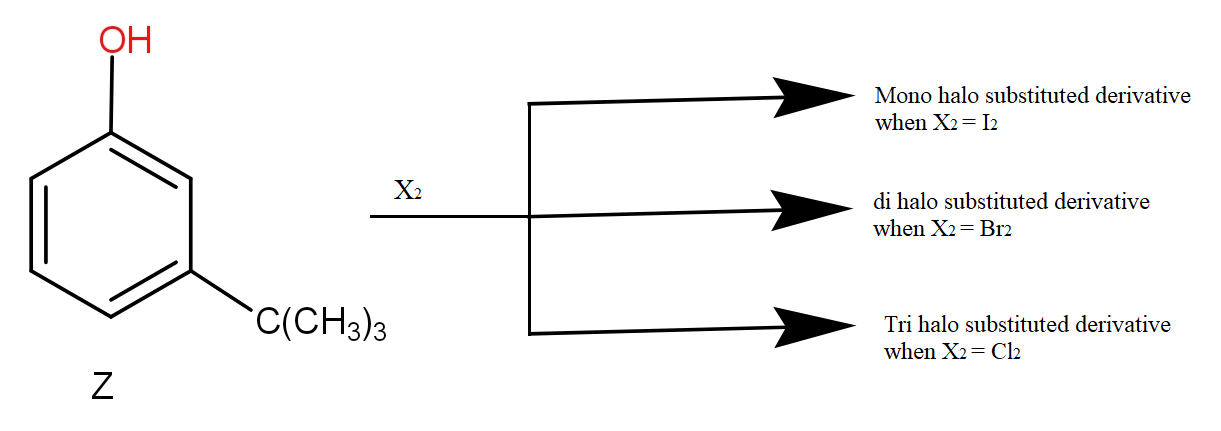
Question: The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given above. Th...
The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given above. The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained by :
a.) the steric effect of the halogen
b.) the steric effect of the tert-butyl group
c.) the electronic effect of the phenolic group
d.) the electronic effect of the tert-butyl group
Solution
The electrophilic substitution reaction is one in which an electrophile replaces or gets substituted on the hydrogen of the benzene ring.
The tert butyl group present is bulky and thus imparts hindrance to the incoming electrophile.
Complete step by step answer:
First, let us see what an electrophilic substitution reaction is. The substitution reaction is the one in which an atom is replaced by any other atom of different element. The electrophile is the electron deficient species. The species that involve electrophile is called electrophilic substitution reactions.
The alkenes normally undergo addition reactions with halogens giving additional products. But benzene rings are extra stable due to resonance. So, it does not give addition reactions because the addition reactions can break its resonance. The benzene undergoes aromatic substitution reactions where a hydrogen is substituted by any other electrophile.
The next thing to observe here in the substrate is the presence of tert butyl group which is a bulky group. This bulky group causes steric hindrance to the incoming electrophile.
The different pattern of halogenation is seen because of steric factors.
The iodine has a large size. Due to steric hindrance of tert butyl group and the large size of iodine, only one atom can get substituted.
The bromine atom is smaller than iodine. It also experiences steric hindrance but due to comparatively small size, two atoms can be substituted.
The chlorine atom is the smallest and thus can substitute three hydrogen atoms.
So, the correct answer is “Option A and B”.
Note: One can say that only tert butyl group causes steric hindrance but we also notice that the size of incoming electrophile also affects the reaction. As the size of iodine was large, so only mono substitution. The Br atom is smaller so di substitution and the Cl is very small in comparison to these two, so tri substitution occurred.
