Question
Question: The reactivities of these ions in azo-coupling reactions will be in the order of: A. 
B.
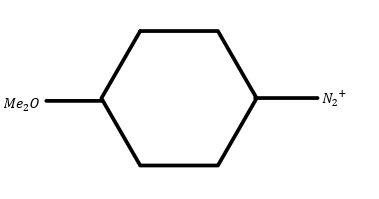
C.
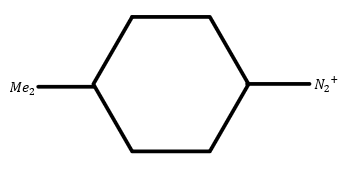
D.
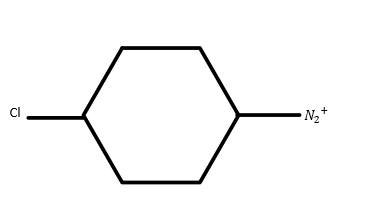
A) 3<1<4<2
B) 1<4<2<3
C) 1<2<3<4
D) 3<1<2<4
Solution
Electron withdrawing groups: The groups which can attract electrons towards itself from the benzene ring, are known as electron withdrawing groups. For example: nitro group. When nitro is attached to a benzene ring then it draws electrons towards itself.
Complete step by step solution:
Ortho position: In a benzene ring when two groups or atoms are at position 1,2 i.e. at adjacent positions, are known as ortho positions. For example: if groups are nitro groups and they placed at position 1,2 then they are said to be ortho nitro benzene.
Meta-position: In benzene rings when two or more groups or atoms are alternate to each other i.e. 1,3 or 1,5 positions, is known as meta-position. For example: if groups are nitro and they are placed at 1,3 or 1,5 positions then they are said to be meta nitro benzene.
Para-position: In a benzene ring when two or more groups or atoms are at opposite positions i.e. 1,6, is known as para-position. For example: if groups are nitro and they are placed at 1,6 positions then they are said to be para nitro benzene.
Now, we discuss electron withdrawing and electron donating groups.
Electron withdrawing groups: The groups which can attract electrons towards itself from the benzene ring, are known as electron withdrawing groups. For example: nitro group. When nitro is attached to a benzene ring then it draws electrons towards itself. Hence it decreases the electron density at the benzene ring. So they are also known as meta directing groups.
Electron donating group: The groups which can donate electrons to the benzene ring, are known as electron donating groups. For example: alkyl groups attached to the benzene act as electron donating groups. They are also known as ortho or para directing groups.
In the azo-coupling process, diazonium ion is present. Now if the electron withdrawing group is present to the ion then it will increase the reactivity and if the electron donating group is present then it will decrease the reactivity.
Now in the molecule (1) two methyl groups are attached so they will act as electron donating groups. Hence its reactivity will be low.
In ion (2) one methyl with oxygen groups is attached so they will act as electron donating groups. Hence its reactivity will be low. But the reactivity will be greater than ion (1).
In ion (3) only one methyl group is attached so it will also act as electron donating groups. Hence its reactivity will be low. But the reactivity will be greater than ion (1) and (2).
In ion (4) chlorine group is attached which is an electron withdrawing group. So the reactivity will be high for ion (4). Hence the order is as: 1<2<3<4.
So option C is correct.
Note: Electrophilic groups: Those groups which can accept electron pairs, are known as electrophilic molecules. They are also known as Lewis acids. For example: carbocations.
Nucleophilic groups: Those groups which can donate electron pairs, are known as nucleophilic molecules. They are also known as Lewis base. For example: Carbanions.
