Question
Question: The reaction, Q to R and R to S, are: 
A. Dehydration and Friedel-Crafts acylation
B. Friedel-Crafts alkylation
C. Friedel-Crafts alkylation, dehydration and Friedel-Crafts acylation
D. Aromatic sulfonation and Friedel-Crafts acylation
Solution
Friedel reaction is the introduction of alkyl or acyl groups into an aromatic structure in the presence of acid catalyst. They are of two types-Friedel Craft acylation and Friedel Craft alkylation.
While dehydration is the process of removal of water molecules from a compound. Aromatic sulfonation is a reaction in which - SO3H group is attached to an aryl group.
Complete step by step solution:
The complete reaction mechanism of production of compounds Q, R, S from compound P is given below:
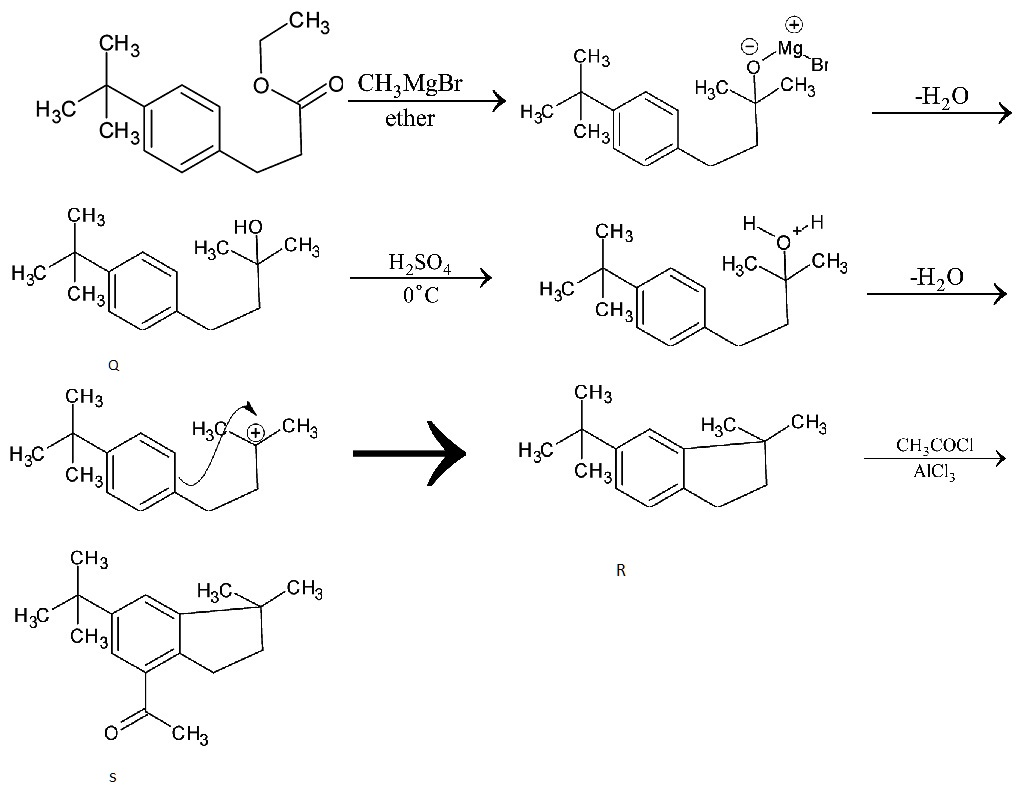
In the initial step, the given compound P is reacted with Grignard reagent, CH3MgBr in the presence of a solvent, ether, C2H5OC2H5. It produces an adduct with the Grignard reagent. It is then undergone hydrolysis which produces alcohol. This is the compound Q. This compound undergoes dehydration reaction in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid. This compound having a carbocation, undergoes further Friedel Craft alkylation in which the compound is reacted with alkyl halide to produce a cyclopentane ring attached to the benzene group. This is further undergone by Friedel Craft acylation in which the compound is reacted with the acyl chloride in the presence of aluminium chloride. It produces an aryl ketone.
Thus the reactions Q to R and R to S involve Friedel Craft alkylation, dehydration and Friedel Craft acylation.
Hence the correct option is C.
Note: Friedel Craft alkylation reaction is a type of electrophilic substitution. It involves an intermediate which is a carbocation. Commonly used alkylating agents are alkyl halides, alkenes, alcohols, etc. Also the most commonly used catalysts should be Lewis acids. They are AlCl3 and BF3.
