Question
Question: The reaction of propene with \[{\text{HOCl }}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{...
The reaction of propene with HOCl (Cl2 + H2O) proceeds through the intermediate:
A.CH3−CH+−CH2−Cl
B.CH3−CH(OH)−CH2+
C.CH3−CH(Cl)−CH2+
D.CH3−CH+−CH2−OH
Solution
The formation of carbocation provides the intermediate stage which can be observed when positively charged chlorine atom attacks on propene.The reaction of propene with HOCl in the presence of Cl2 + H2O is an addition reaction. HOCl contains OH− and Cl+.
Step by step answer: The structure of propene is CH3−CH=CH2. Propene reacts with HOCl as follows:
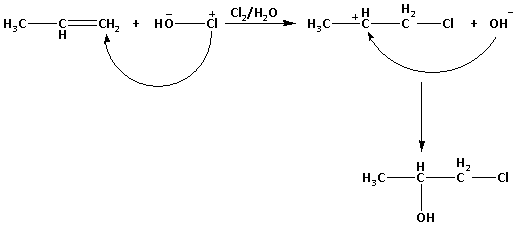
The HOCl contains OH− and Cl+.
In the first step of the reaction, the positively charged Cl+ attacks the carbon-carbon double bond. This results in formation of a carbocation intermediate CH3−CH+−CH2−Cl.
In the second step of the reaction, the nucleophile OH− attacks the positively charged carbon atom. The final product obtained is CH3−CH(OH)−CH2−Cl.
Thus, the reaction of propene with HOCl (Cl2 + H2O) proceeds through the intermediate CH3−CH+−CH2−Cl.
Thus, the correct option is (A) CH3−CH+−CH2−Cl.
Additional Information: The reaction in which one molecule combines with another molecule to form a larger molecule is known as an additional reaction. No products are eliminated in the addition reaction.
There are two types of addition reactions:
Electrophilic addition reaction: In electrophilic addition reaction, a positively charged species known as electrophile gets added to a molecule.
Nucleophilic addition reaction: In nucleophilic addition reaction, a negatively charged species known as nucleophile gets added to a molecule.
The product formed in the reaction is 1-chloropropan-2-ol. 1-chloropropan-2-ol is an alcohol. Thus, the reaction is a preparation reaction of alcohol.
Note: A positively charged carbon atom is known as a carbocation.
When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to only one alkyl group it is known as a primary carbocation. Thus, CH3−CH(Cl)−CH2+ is a primary carbocation.
When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to two other alkyl groups it is known as a secondary carbocation. Thus, CH3−CH+−CH2−Cl is a secondary carbocation.
A secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation. Thus, CH3−CH+−CH2−Cl is formed as an intermediate.
