Question
Question: The reaction of propene with \[HOCl\] proceeds via the addition of: (A) \[{H^ + }\] in first step ...
The reaction of propene with HOCl proceeds via the addition of:
(A) H+ in first step
(B) Cl+ in the first step
(C) HO− in first step
(D) Cl+and HO− in the first step
Solution
Propene is known as methyl ethylene or propylene. Propene is having the suffix ‘ene’. Therefore, we can say that it belongs to the alkene group and it is the second member of the alkene group. Propene is having a double bond. Propene is an unsaturated compound and is having the molecular formula of CH3−CH=CH2. Alkene will undergo electrophilic addition reaction.
Complete Solution :
- Propene is an organic compound which belongs to the family of alkene. The molecular formula of Propene is CH3−CH=CH2. Propene is an unsaturated compound because it contains a double bond. Propene will undergo electrophilic addition reaction in order to form the addition product. When the electrophile attacks the C-C double bond present in the alkene, it will get converted into a single bond. HOClis a hypochlorous acid, it will break into HO−and Cl+, where Cl+ is the electrophile. This is because Oxygen is more electronegative compared to chlorine. Therefore, oxygen will have the negative charge and chlorine will have the positive charge.
- The HOCl will be formed from the chlorine molecule and water. The formed HOCl will split into HO− and Cl+ ions. According to Markonikov’s rule, when the polar compound like HOCl is added to propene, the positive part, i.e. Cl+ will be attached to the carbon with higher number of hydrogen atom and the negative part, i.e. HO− will be attached to the carbon with lesser number of hydrogen across the double bond. The compound formed will be 1-Chloropropan-2-ol.
The Electrophilic addition reaction takes place in two steps:
First step is the attack of the electrophile, i.e. Cl+
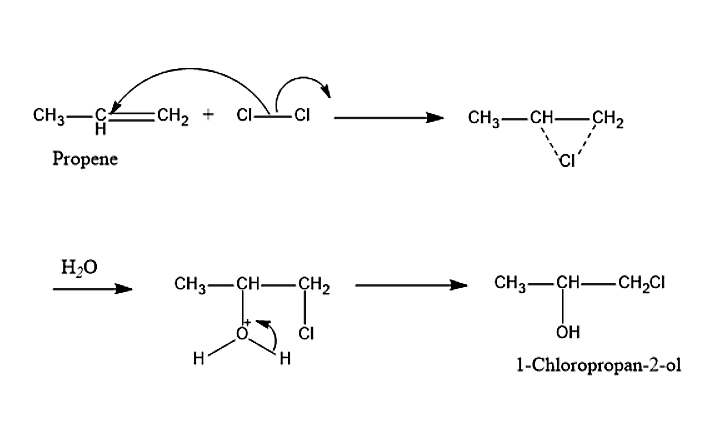
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Alkene undergoes addition reaction instead of substitution reaction. This is because alkenes are less stable compared to alkanes. In order to break the bonds that are present in alkene, it will require more energy than that is required to make a new bond.
