Question
Question: The reaction of alkoxide ion with alkyl halide to form ether is known as: (A) Wurtz reaction (B)...
The reaction of alkoxide ion with alkyl halide to form ether is known as:
(A) Wurtz reaction
(B) Kolbe’s reaction
(C) Williamson’s synthesis
(D) Perkins reaction
Solution
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula R–O–R′, where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been given that alkoxide ion reacts with alkyl halide to form ethers,
An alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as RO−, where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands.
The haloalkanes are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names.
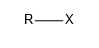
We need to name the reaction,
The reaction of alkoxide ion with alkyl halide to form ether is known as Williamson's synthesis.
Williamson's synthesis is used to prepare diethyl ether.
This is the industrial process for making ethers.
Sodium ethoxide is heated with ethyl iodide to form diethyl ether,
C2H5ONa+C2H5I→C2H5−O−C2H5+NaI
Therefore, we can conclude that option (C) is correct.
Note: The other options given in the question are:
-Wurtz's reaction is an organic chemical coupling reaction wherein sodium metal is reacted with two alkyl halides in the environment provided by a solution of dry ether in order to form a higher alkane along with a compound containing sodium and the halogen.
-The Kolbe–Schmitt reaction or Kolbe process is a carboxylation chemical reaction that proceeds by heating sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide under pressure, then treating the product with sulfuric acid. The final product is an aromatic hydroxy acid which is also known as salicylic acid.
-The Perkin reaction is an organic reaction developed by English chemist William Henry Perkin that is used to make cinnamic acids.
