Question
Question: The \[R\] and \[S\] enantiomers of an optically active compound differ in: A. their reactivity wit...
The R and S enantiomers of an optically active compound differ in:
A. their reactivity with chiral reagents.
B. their melting points.
C. their optical rotation of plane polarized light.
D. their solubility in chiral reagents.
Solution
When a compound is non-super imposable on its mirror image, the compound would be chiral and it will exhibit optical isomerism. All chiral objects rotate plane polarized light.
Complete step by step answer:
TheR andS enantiomers are the optical active substances; they differ in their optical rotation of plane polarized light.
Enantiomers have identical physical properties such as densities, boiling points, melting points and enantiomers rotate plane polarized light in equal and opposite directions. These are called optical Isomers. But we know, enantiomers are a pair of molecules that exist in two forms that are mirror images of one another but cannot superimpose each other. A pair of enantiomers is distinguished by the direction in which when dissolved in solution, they rotate plane polarized light either clockwise direction then it is dextrorotatory (d or +) or anticlockwise direction then it is levorotatory (l or −).
Examples of the R and S configuration are sulfur and phosphorus chiral centers are given below:
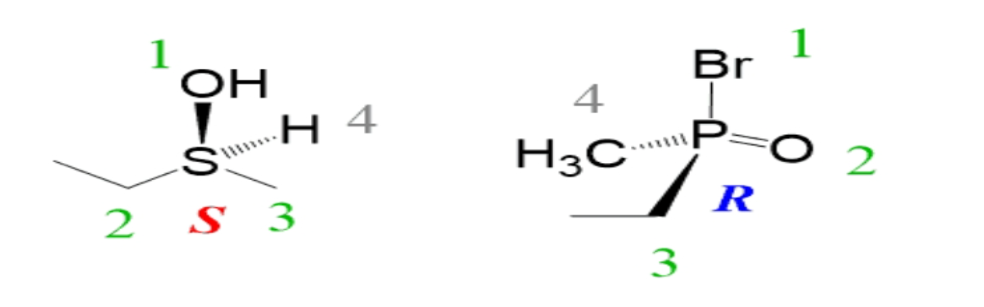
Hence the correct option is (C).
Note: R andS configuration represent the right hand and left-hand nomenclature, and are used to name the enantiomers of a chiral compound. R and S notation uses the CIP priority rules for the assignment of the absolute configuration around a stereo center. Enantiomers are two molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images. Enantiomers are called stereoisomers. All chirality center are inverted in enantiomers, every R is changed to S and every S is changed into anR.
