Question
Question: The product (A) and (B) are respectively:  and (B) are respectively:
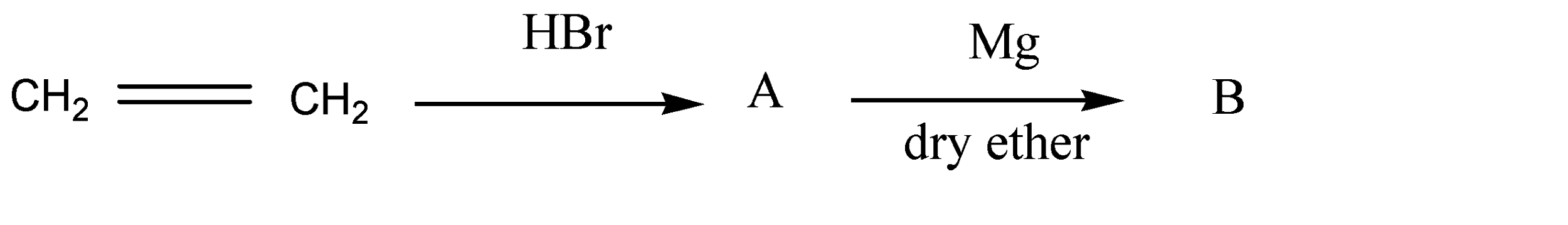
Solution
Ethene is symmetrical alkene which contains two carbon atoms. In presence of HBr, ethene will give bromoethane as the product. This reaction is an additional reaction. In presence of organic peroxide, the halogen adds with the carbon in double bond having greater number of hydrogen atoms. It is anti markovnikov addition. It is called the Kharasch effect.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know ethene has two carbon atoms which are symmetrical alkene. Ethene reacts with HBr and gives ethyl bromide in the first step as a product. The reaction is given below:
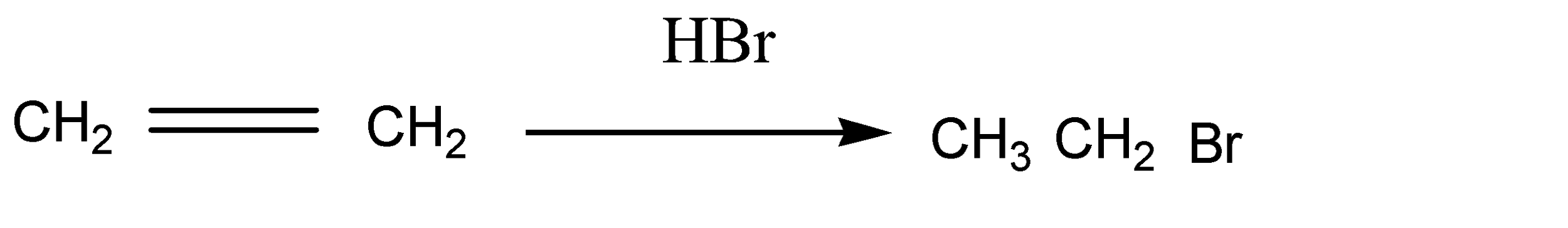
HBr molecules are added across the double bond. Here the anti markovnikov rule is assumed because the molecule is symmetrical around the double bond. Otherwise the number of hydrogen atoms belonging to double bond carbon atoms are equal.
In the next step, bromoethane reacts in the presence of Mg and dry ether and forms a new product. Here the reaction is given below:
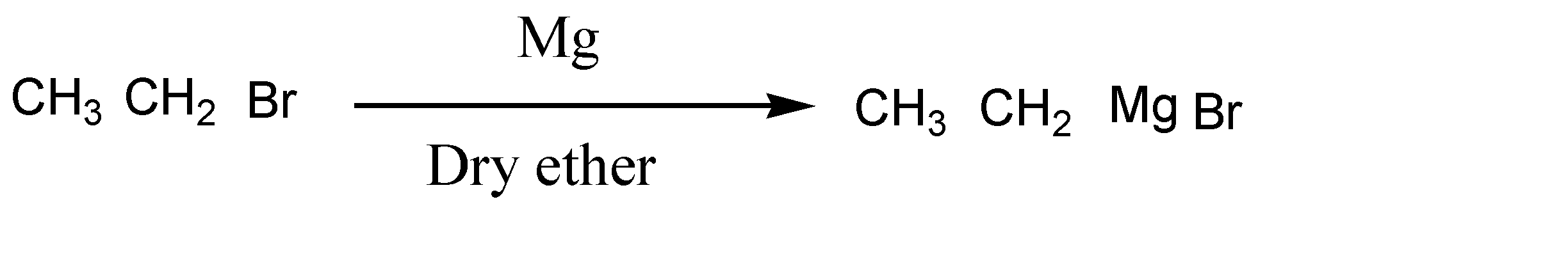
Here bromo ethane reacts with Mg in presence of dry ether and forms ethyl magnesium bromide.
So, the reaction is given as below:
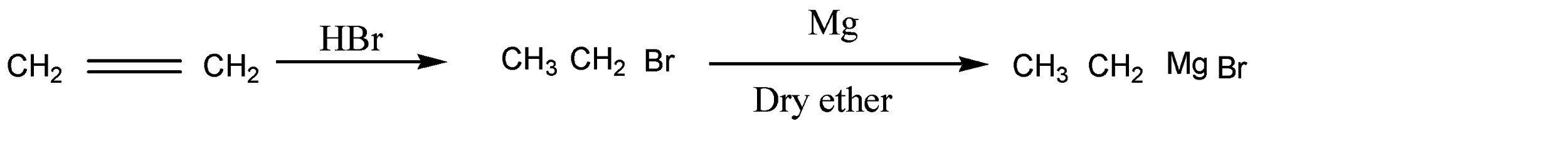
So here product A is bromoethane and product B is ethyl magnesium bromide.
Note: HBr adds to alkenes to create alkyl halides. A good way to think of the reaction is that the pi bond of alkene acts as a weak nucleophilic and reacts with the electrophilic proton with HBr. These are really just two ways to think about the same event. Either way a carbocation intermediate is formed along with the bromide anion during the initial step of reaction.
