Question
Question: The process of reaction, \(A \rightleftharpoons nB\) with time, is represented in the figure, given....
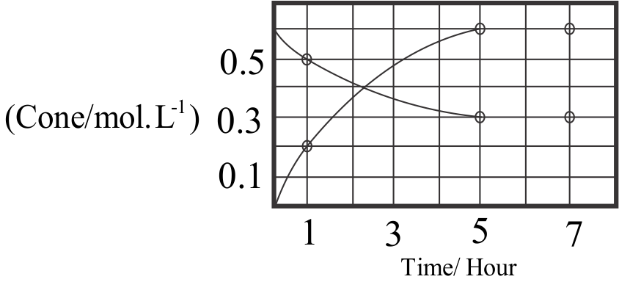
The process of reaction, A⇌nB with time, is represented in the figure, given. Determine the initial rate of conversion of A .
Solution
The initial rate of change for the concentration of A can be given according to the rate of change in concentration with respect to time. The initial rate can be defined for the first part of the reaction process starting from the start of the reaction to only unit time measurements.
Complete step by step answer:
- The rate of change in concentration of A defines the conversion level of A⇌nB . The changing concentration for the first hour is found to be changed to 0.2molL−1 from the initial rate which is 0molL−1 according to the given graphical representation. This change in the concentration takes place over a time of around the first hour.
- This is considered as the initial 1hour of the reaction which defines the time for finding out the initiate rate of the reaction. Since this is a reversible reaction there are two molecules involved in the process which are A and B . Therefore, the rate of change takes place for both the molecules in the reaction process.
- The graph depicts the concentration for both the molecules changing with respect to time in hours. The equation for finding out the initial rate of conversion of A is:
For any given reaction process, Rate=ΔTimeΔConcentration .
Here the initial concentration needs to be found out and that is why change is taken for the first 1hour as given below, Therefore the resultant initial rate for conversion of A :
Rate=1−00.2−0
- Therefore, calculating the value the conversion rate will be 0.2molL−1hour−1 . The initial process of conversion may be different from the rates at the final level. This is why only the change for 1hour is chosen.
Note: The rate of the reaction can be easily measured based on the concentration to time ratio based on different time intervals. The level of product formation depends on the type of reaction (reversible or non-reversible). In some reactions, the rate is different at different levels but in some of them, the rate remains constant.
