Question
Question: The process involved in the conversion of oils into fats is: A.Hydrolysis B.Oxidation C.Esteri...
The process involved in the conversion of oils into fats is:
A.Hydrolysis
B.Oxidation
C.Esterification
D.Hydrogenation
Solution
The process which is involved to convert oils into fats is known as hydrogenation. In Hydrogenation, liquid vegetable oil is converted into solid or semi-solid fats at a very high temperature. When the degree of saturation of the fat is changed, then some important physical properties such as the melting range is also changed, which is the reason why liquid oils become semi-solid trans fats.
Complete step by step answer:
Fats and oils are the lipids which are most abundant in nature. They help to provide energy for living organisms, insulate body organs, and transport fat-soluble vitamins through the blood. Fats and oils are called triglycerides or triacylglycerols because they are esters which are composed of 3 fatty acid units joined to glycerol which is a trihydroxy alcohol.
In fats and oils, double bonds can undergo hydrogenation and also oxidation. In the food industry, the hydrogenation of vegetable oils to produce semi solid fats is an important process. It is essentially identical to the catalytic hydrogenation reaction described for alkenes chemically.
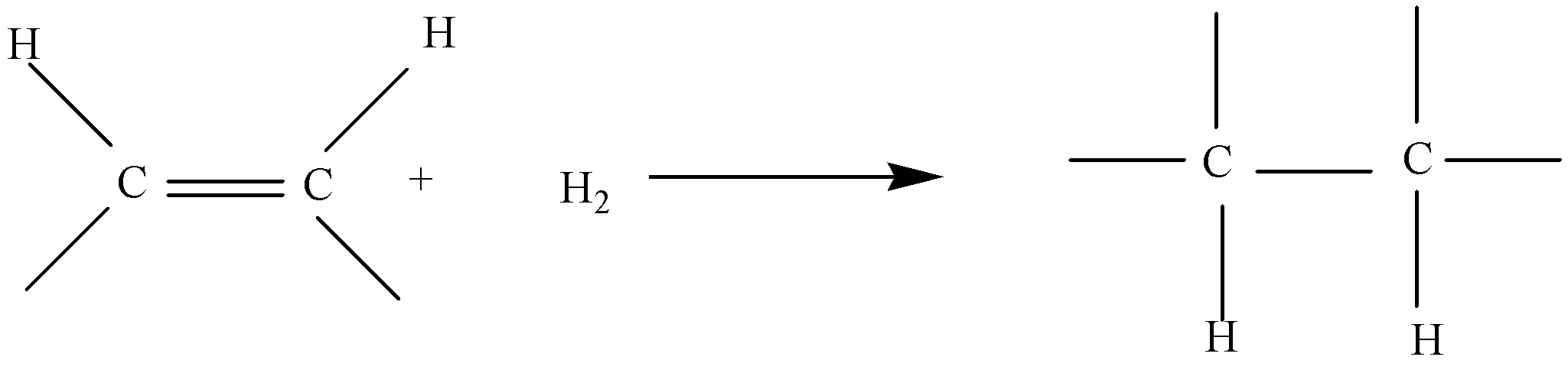
In commercial processes, the number of double bonds that are hydrogenated is carefully controlled to produce fats with the desired consistency which is soft and pliable. Inexpensive and abundant vegetable oils like canola, corn, soybean are thus transformed into margarine and cooking fats.
So, the process involved in the conversion of oils into fats is hydrolysis.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: It should also be noted that fats and oils that are in contact with moist air at the room temperature eventually undergo oxidation and hydrolysis reactions and because of that they turn rancid, acquiring a characteristic disagreeable odour. The release of volatile fatty acids by hydrolysis of the ester bonds is also the cause of the odour. For example, butter releases foul-smelling butyric, caprylic, and capric acids.
