Question
Question: The possible blood groups of the offspring of the parents with blood group O and AB are (А) O, A,...
The possible blood groups of the offspring of the parents with blood group O and AB are
(А) O, A, B and AB
(B) A, B and AB
(С) A and B
(D) O and AB
Solution
Mendel also conducted artificial pollination or cross-pollination experiments using several true-breeding pea lines. In this case, the alleles show codominance.
Complete answer: Mendel selected a total of 14 true-breeding pea varieties. He selected 7 characters, some of them include seed shape, seed colour, pod colour, etc. Mendel crossed pea plants, for instance, stem height and crossed with tall and dwarf plants and got a ration 3:1, but some inheritance differs from this ratio as:
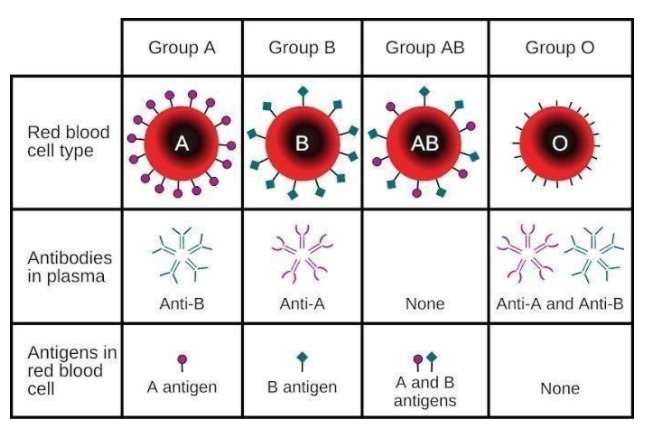
Codominance:
ABO blood type is an ideal example of co-dominance. For ABO blood group system of blood groups, allele A produces N-acetylgalactosamyl transferase enzyme which recognises H antigen present in RBC membrane and adds N-acetylgalactosamine to sugar a part of H antigen to make A antigen. The allele IB produces galactosyl transferase enzyme which adds galactose to sugar a part of H-antigen to make B antigen. Alleles 14 and 15 produce a rather different sort of sugar, while allele i don’t produce any sugar or antigen. IA and i are completely dominant over i, in other words when IA and i are known to occur only if IA expresses, as i don’t produce any sugar, and when IB and i are present, only 1B expresses. When both IA and i are present, both enzymes or sugars both antigens A and B are produced, which is often due to codominance. These antigens determine the sort of blood type. Blood type A has antigen A, B has antigen B, AB has both antigens, while blood type O doesn't carry any antigen. So, the child can have blood type A or B which differs from parents.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Besides incomplete dominance, certain alleles show codominance. Here in F1 hybrid, both alleles express themselves equally and there is no mixing of the effect of both alleles, therefore, the hybrid progeny (F1) resembles both the parents.
