Question
Question: The position (\(x\) ) - time (\(t\) ) graph of a particle of mass \(1kg\) moving along in x-directio...
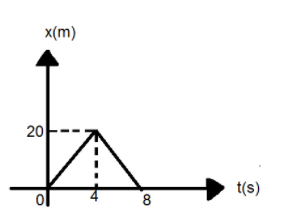
The position (x ) - time (t ) graph of a particle of mass 1kg moving along in x-direction is shown in the figure. find the impulse of the particle at t=4s.
Solution
Impulse defined the overall effect of force acting over time. Impulse is important because real-world forces are not constant mostly, for example, forces due to people or engines are changed with time and can rely on many factors. Impulse can also be known as a change in momentum.
Complete step by step solution:
Impulse (J)=F.Δt………………. (1)
Δp=F.Δt……………. (2)
J=Δp
J=pf−pi ……………… (3)
Where Δp the change in momentum is, pf is final momentum, pi is initial momentum, F is the force, Δt is the time difference
From equation (3) J=pf−pi
Where pi=mvi …….. (4)
vi=tixi=420
m=1kg
Put these values in equation (4)
We get pi=5kgm/s
Similarly pf=mvf
vf=4−20
pf=−5kgm/s
Change in momentum = impulse
pf−pi=J
J=−5−5
J=−10kgm/s
Note:
When we find the value of impulse we multiply force with time difference which is similar to finding the area under the force-time curve. This is useful since the area can easily be calculated for a complicated curve as for a simple curve.
The concept of impulse internal or external is fundamental to understanding the change in momentum.
Specific impulse commonly used when an engine produces thrust Force, it is mostly used in jet engines and rocket engines. It is the measure of the efficiency of using fuel to produce thrust.
