Question
Question: The \[pKa\] of acetyl salicylic acid (aspirin) is \[3.5\]. The \[pH\] of gastric juice in the human ...
The pKa of acetyl salicylic acid (aspirin) is 3.5. The pH of gastric juice in the human stomach is about 2−3 and the pH in the small intestine is about 8. Aspirin will be:
A.unionised in the small intestine and in the stomach
B.completely ionised in the small intestine and in the stomach
C.ionised in the stomach and almost unionised in the small intestine
D.ionised in the small intestine and almost unionised in the stomach
Solution
Aspirin is weakly acidic in nature. But the dissociation or ionisation of aspirin is more favorable in the basic environment. It will not ionise in an acidic environment as the concentration of hydrogen ions is more.
Complete step by step answer:
Aspirin is a compound which is synthesized using salicylic acid and acetic anhydride or acetyl chloride.
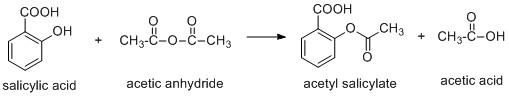
The aspirin is a weak acid and it undergoes ionisation to produce hydrogen ion.
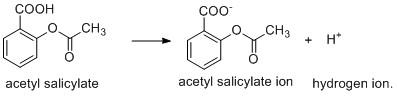
The above ionisation is possible when the products formed i.e. H+ ion is consumed or removed from the system to generate other products. The pH of the small intestine is 8 which indicates that it is basic in nature. As pKa of aspirin is greater than the pH of small intestine, so the former undergoes ionisation in small intestine by combination of H+ and basic OH− ion generating water molecule.
The above ionisation is not possible where there is presence of H+ ion in excess. This can be accounted for by the common ion effect. The common ion effect describes that when a common ion viz. H+ is already present in the medium such dissociation is unfavorable and it will prevent the forward reaction. As pH in the stomach is 2−3 which indicates that pH>pKa, so the ionisation will not occur.
Hence the correct option is D. Aspirin will be ionised in the small intestine and almost unionised in the stomach.
Note:
The acidity is the property of acids and is defined by the ability to give hydrogen ions in an acid base reaction. The basicity is the property of bases to accept the hydrogen ion in a reaction.
