Question
Question: The person looks at the image of two parallel finite length lines PQ and RS in a convex mirror (see ...
The person looks at the image of two parallel finite length lines PQ and RS in a convex mirror (see figure).Which of the following represents schematically the image correctly?

(Note: Letters P, Q, R and S are used only to denote the endpoints of the lines.)
A. Fig A
B. Fig B
C. Fig C
D. Fig D
Solution
Hint: - Use properties of curved mirrors and also use the law of reflection for correct tracing the path of rays after reflection. Use properties of point size objects by considering each point on lines as point sized objects. We can easily solve this by using the concept that the angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According the given question
Here, lines PQ and RS are parallel to the principal axis of the mirror and also parallel to each other. So, if we consider any point on lines as point sized object placed in front of the mirror, then we can easily trace the path of rays emerging from that point sized object by using simple properties of mirror and using laws of reflections which as follow:
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
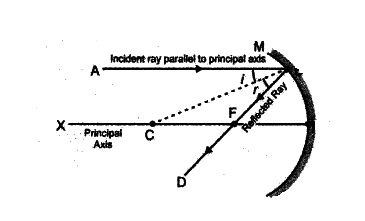
∴∠i=∠r
Now by using basic knowledge of ray diagrams and properties of mirrors we track the path of rays after reflection.
The parallel rays emerging from that point will converge on principal focus after reflection from the mirror because we know that parallel lines to the principal axis will converge on principal focus after reflection.
So, similarly all points on the both lines will try to converge towards the focus after reflection hence both lines will seem in converging nature after reflection.
Also, point P and R nearer to the surface of the mirror will remain nearer to the surface even after reflection and Q and S remains farther.
So, the image of lines formed as shown in figure (B).
∴Correct answer is B.
Note: The points near the surface of the mirror remain near to the surface only. The image result of an object reflected by a convex mirror is typically virtual, upright, and smaller. Discover how moving the object farther away from the mirror's surface affects the size of the virtual image formed behind the mirror.
