Question
Question: The perimeter of a sector is constant. If its area is to be maximum, then the sectorial angle is A...
The perimeter of a sector is constant. If its area is to be maximum, then the sectorial angle is
A. 2π
B.4π
C.4c
D.2c
Solution
Firstly, we will let the radius be r and sectorial angle be θ . Given that, the perimeter of the sector is constant. Substitute the value of radius in the formula of area of the sector. Then, differentiate both sides with respect to θ . As the area is maximum so, we will put the differential value equal to zero and obtain the value of θ. If the differentiated value is negative, then the area is maximum and the value of θ is correct otherwise not.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let that the radius of the circle is r and the sectorial angle be θ .
We draw a figure,
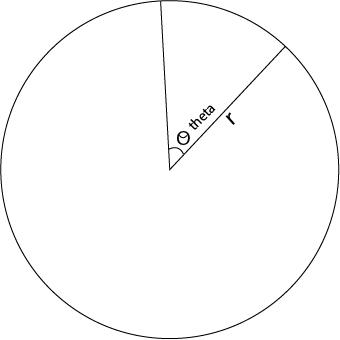
Now, the perimeter of the sector is given by 2r+rθ , according to the question, the perimeter of the sector is constant.
2r+rθ=k
We will evaluate the value of r ,
⇒r=2+θk
The area of sector is denoted by A and given by
A=21r2θ
Now, substitute the value of radius of the above formula of area,
We get,
A=2k2×(θ+2)2θ
We will differentiate the area on both side with respect to θ using the formula,
dxd(vu)=v2v(dxdu)−u(dxdv)
We get,
\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dA}}{{d\theta }} = \dfrac{{{k^2}}}{2}\left\\{ {\dfrac{{{{(\theta + 2)}^2} - 2\theta (\theta + 2)}}{{{{(\theta + 2)}^4}}}} \right\\} \\\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dA}}{{d\theta }} = \dfrac{{{k^2}}}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{(\theta + 2)(\theta + 2 - 2\theta )}}{{{{(\theta + 2)}^4}}}} \right) \\\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dA}}{{d\theta }} = \dfrac{{{k^2}}}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{2 - \theta }}{{{{(\theta + 2)}^3}}}} \right)...........eq(1) \\\
\
The area has to be maximum so, we will put the value of dθdA written as equation (1) equal to zero.
We get,
⇒dθdA=0 ⇒2k2((θ+2)32−θ)=0 ⇒2−θ=0 ⇒θ=2
Again differentiate the equation (1) with respect to θ , we get,
⇒dθ2d2A=2k2(θ−2)42(−3)−[(θ+2)3]2(θ+2)3×1−θ×3(θ+2)2 ⇒dθ2d2A=2k2[(θ+2)4−6−(θ+2)4θ+2−3θ] ⇒dθ2d2A=2−k2[(θ+2)46+(θ+2)42−θ]
Now, we will substitute the value of θ=2
We have,
⇒dθ2d2A=2−k2[(2+2)46+(2+2)42−2] ⇒dθ2d2A=2−k2[(4)46+0] ⇒dθ2d2A=256−3k2 ⇒dθ2d2A≺0
We can conclude that the area is maximum as the double derivative of the area is negative at θ=2C .
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Note: When we remember that the area is maximum when the double derivative is negative and minimum when the double derivative is positive.
We need to find the value of θ to determine that the double derivative is negative or positive. we have to remember the formula of area and the perimeter of the sector.
