Question
Question: The p-v diagram of 2g of helium gas for a certain process A→B is shown in the figure below. What is ...
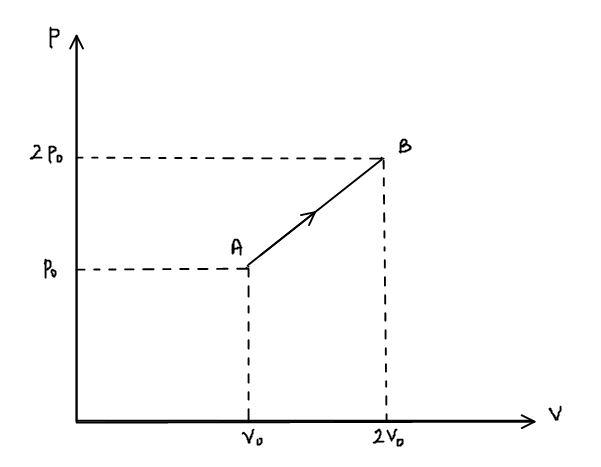
The p-v diagram of 2g of helium gas for a certain process A→B is shown in the figure below. What is the heat given to the gas during the process A→B?
A. 4p∘V∘
B. 6p∘V∘
C. 4.5p∘V∘
D. 2p∘V∘
Solution
In such types of questions, students should observe which type of process the graph is following and also the initial and final coordinates of the process given in the graph.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Step 1:
As the gas is helium and the degree of freedom for helium gas is 3, i.e. F=3.
Here, F is a degree of freedom.
Step 2:
Due to change in process, there will be change in internal energy of the gas, so let’s calculate the change in internal energy of the gas,
The change in internal energy of the gas is given by,
ΔU=2F⋅Δ(P⋅V)
Here, Δ(P⋅V) is P2⋅V2−P1⋅V1 which can be calculated from the given graph.
And F is the degree of freedom and ΔU is a change in internal energy of the gas.
Substituting the value of Δ(P⋅V), the relation becomes,
ΔU=2F⋅(P2⋅V2−P1⋅V1)
Step 3:
The value of P2=2p∘, V2=2V∘, P1=p∘ and V1=V∘ substituting these values in the above relation,
We get,
\Delta Q = \dfrac{3}{2} \cdot \left( {{p_ \circ } \cdot {V_ \circ }} \right) + \dfrac{9}{2} \cdot \left( {{p_ \circ } \cdot {V_ \circ }} \right) \\
\Delta Q = \dfrac{{12}}{2} \cdot \left( {{p_ \circ } \cdot {V_ \circ }} \right) \\
\Delta Q = 6 \cdot \left( {{p_ \circ } \cdot {V_ \circ }} \right) \\
