Question
Question: The oxidation state of nitrogen in: a.) \[{{N}_{3}}H\] b.) \[N{{H}_{3}}\] c.) \[N{{H}_{2}}OH\]...
The oxidation state of nitrogen in:
a.) N3H
b.) NH3
c.) NH2OH
d.) N2H4
Solution
Nitrogen compounds exhibit oxidation states ranging from −3 (ammonia or amines) to +5 (nitric acid).
The electronic configuration of nitrogen is:1s22s22p3
Nitrogen has 5 outer valence electrons, and the three electrons in 2p orbital are unpaired. Nitrogen can gain three electrons (into 2p orbital) or lose all the 5 valence electrons (from 2s and 2p orbitals) to obtain stable configuration.
Complete answer:
We have to calculate the oxidation states of nitrogen in the given compounds.
The given compounds are
N3H- Hydrazoic acid.
NH3- Ammonia
NH2OH- Hydroxylamine
N2H4- Hydrazine
The oxidation state of nitrogen in N3H is as follows.
There are three nitrogen atoms and one hydrogen atom. So,
3x+1 = 0
x = −31
The oxidation state of nitrogen in N3His −31.
The oxidation state of nitrogen in NH3 is as follows.
There is one Nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms. So,
x+3(1) = 0
x+3 = 0
x = -3
The oxidation state of nitrogen in NH3is -3.
The oxidation state of nitrogen in NH2OH is as follows.
The structure of NH2OH is
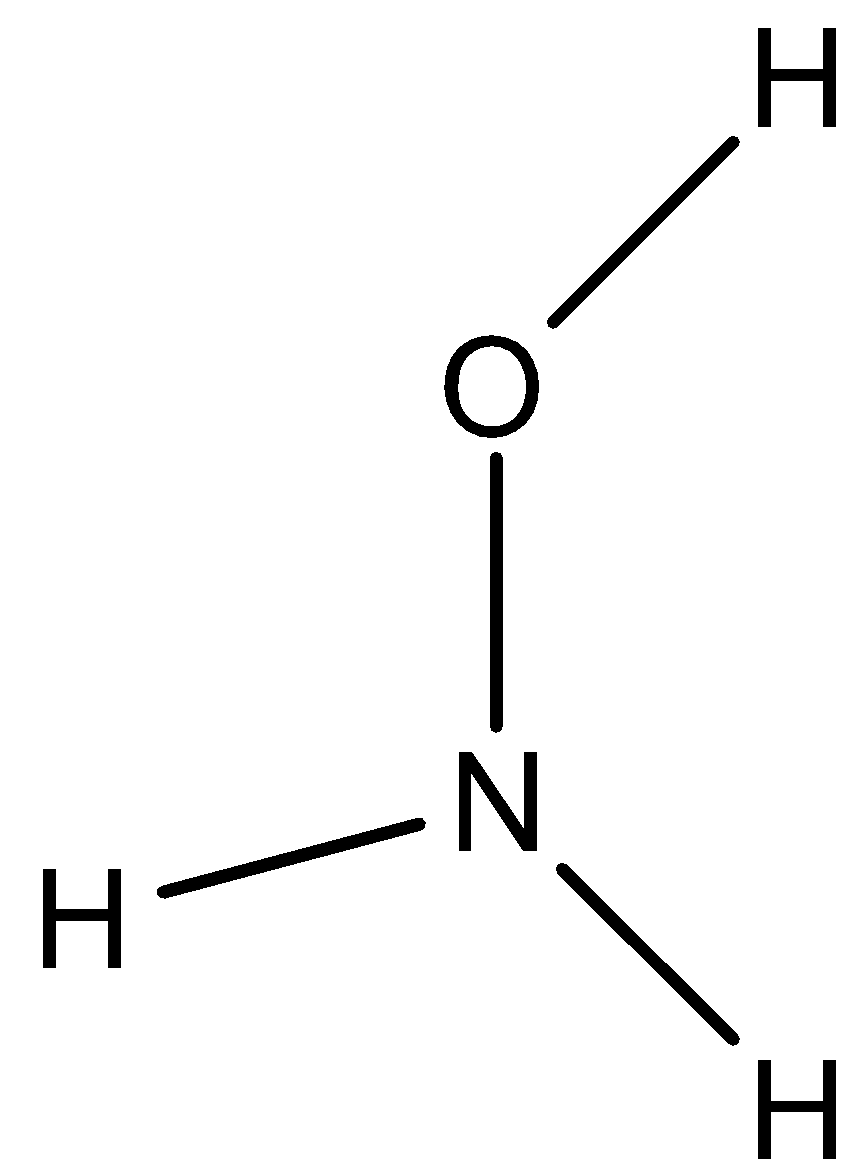
We know that there is one hydrogen atom, one oxygen atom and two types of hydrogen atoms.
One type of hydrogen atom (two hydrogens) directly attached to nitrogen and the second type of hydrogen attached to oxygen atom.
x + 3 (+1) – 2 = 0
x = -1
The oxidation state of nitrogen in NH2OHis -1.
The oxidation state of nitrogen in N2H4is as follows.
There are two Nitrogen atoms and four hydrogen atoms.
2x + 4(1) = 0
2x = - 4
x = -2
The oxidation state of nitrogen in N2H4 is -2.
Note: The various oxidation states of nitrogen are due to the presence of 5 valence electrons. It can donate 5 electrons or it can accept three electrons from other atoms to form stable molecules.
