Question
Question: The number of structural isomers for \({{C}_{6}}{{H}_{14}}\) is: A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 3...
The number of structural isomers for C6H14 is:
A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 3
Solution
Try to recall that structural isomers are compounds that are identical in formula but different in structure or spatial arrangement. Now, by using this you can easily find the correct option from the given ones. Consider differentiating based on the presence of primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary carbon atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
- We know that alkanes with four or more carbon atoms can form structural isomers and those with seven or more carbon atoms can also form optical isomers.
- C6H14 is the sixth member of a homologous series of alkanes and its common name is hexane.
- We know that a primary carbon is attached to 1 other carbon atom, a secondary carbon is attached to 2 other carbon atoms, a tertiary carbon is attached to 3 other carbon atoms, and the quaternary carbon is attached to 4 other carbon atoms.
- First, let us consider the molecules that have only primary and secondary carbon atoms. There will only be 1 isomer of this type that has the name n-hexane or hexane. The structure is:
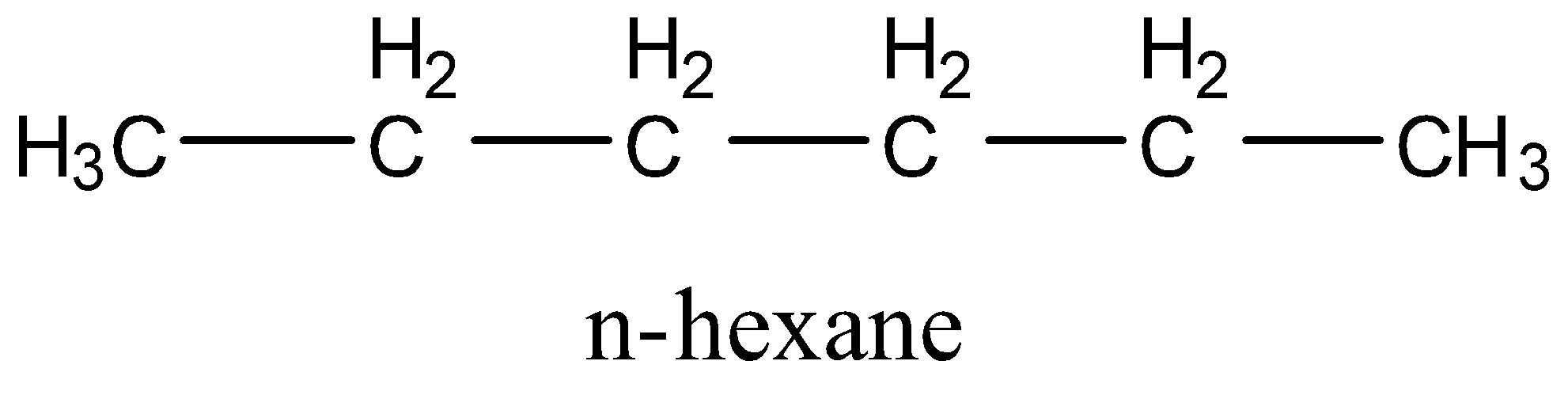
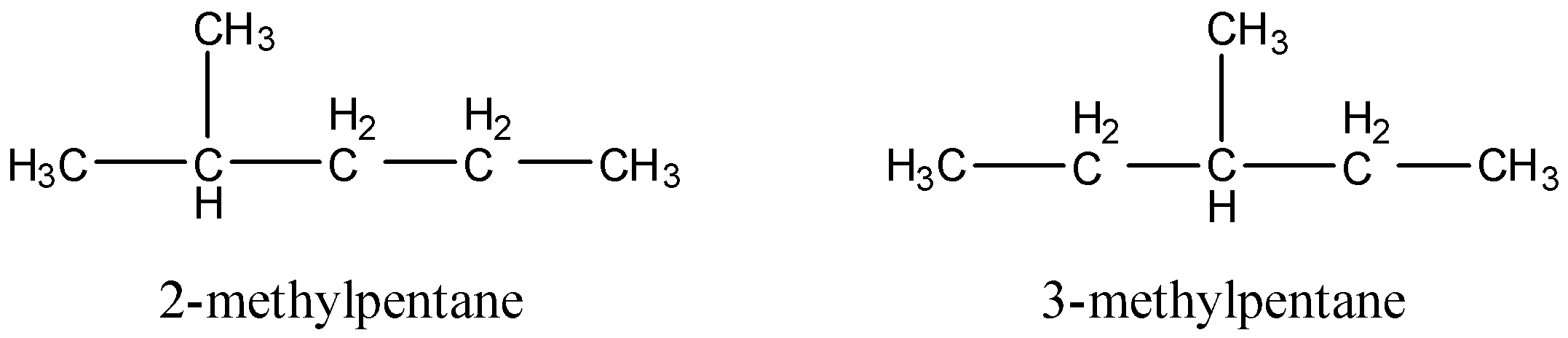
- Now we will consider the isomers that will have 1 tertiary carbon atom. There will be 2 isomers of this type. One is isopentane or 2-methylpentane, and 3-methylpentane. The structures are:
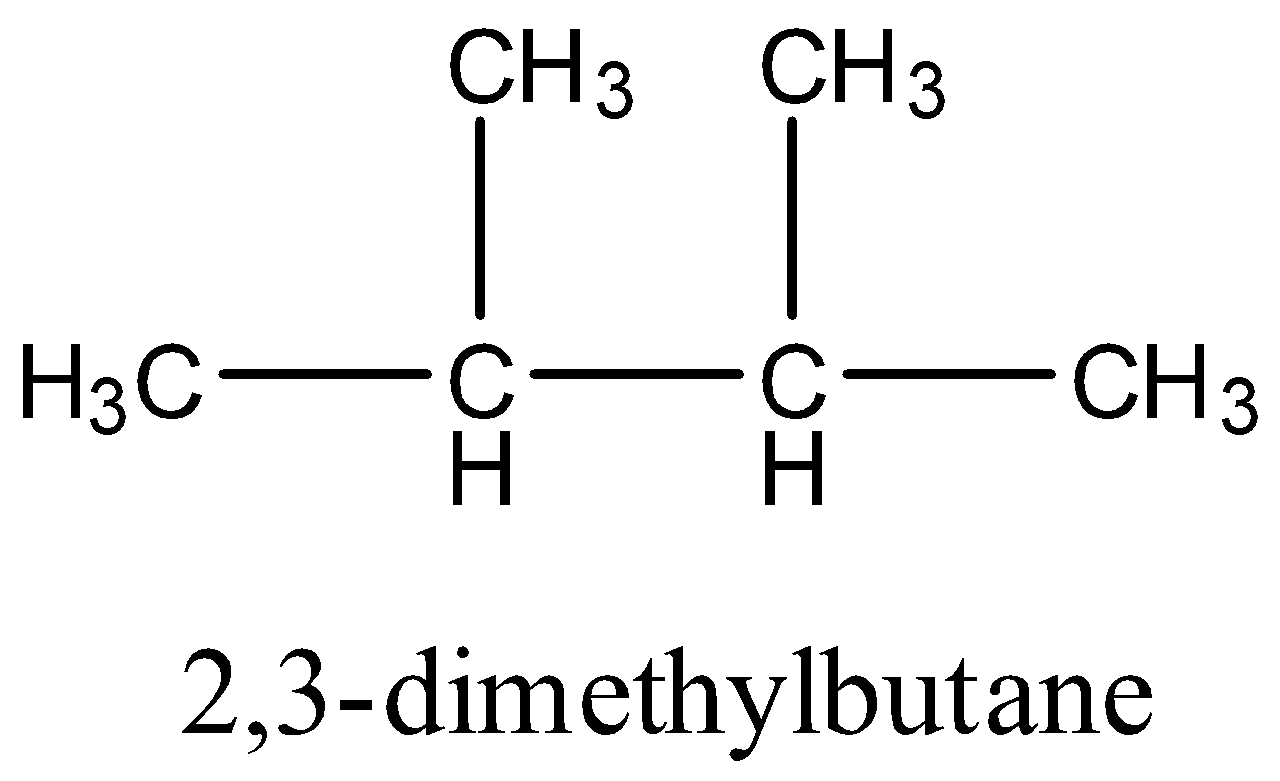
- Now, let us consider the isomers that will have 2 tertiary carbon atoms. Only 1 such structure will be possible whose name is 2,3-dimethylbutane. The structure is:
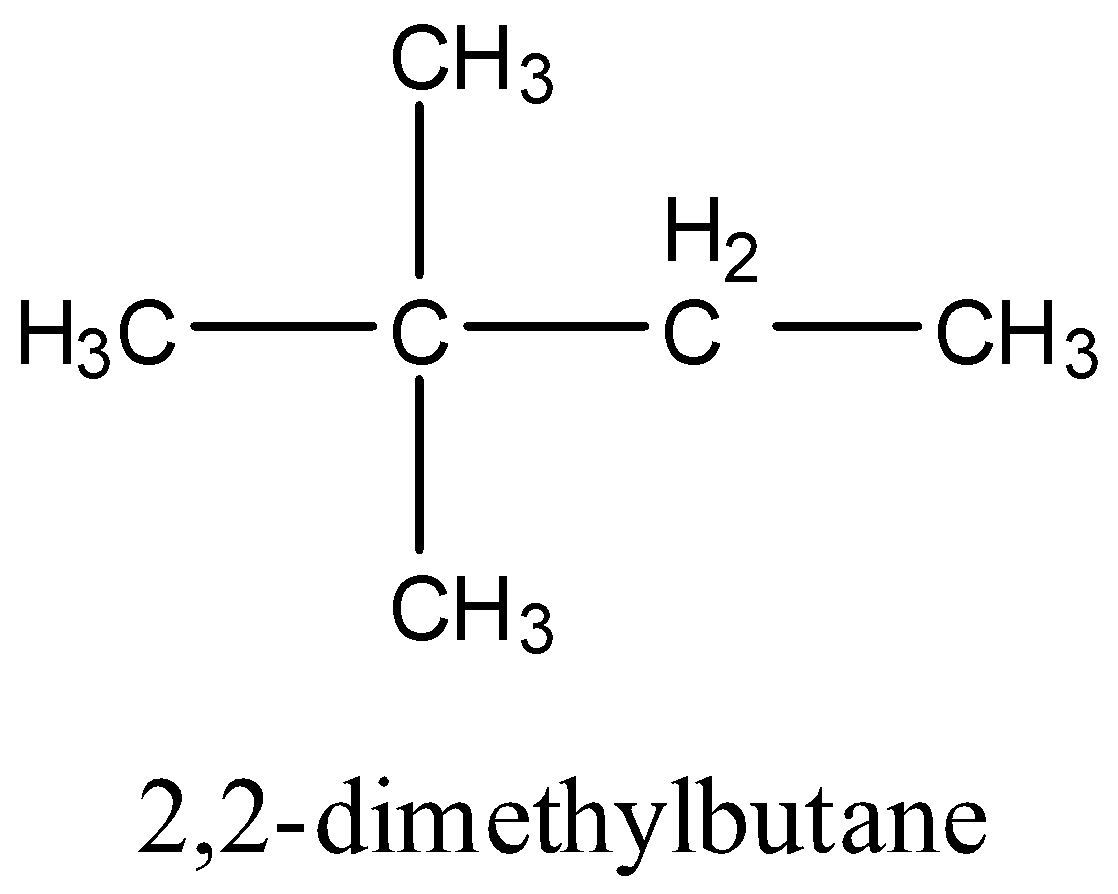
- And finally, we will consider the isomer that has a quaternary carbon. Only one compound of this type will be possible and its name will be neo-hexane or 2,2-dimethylbutane. The structure will be:
- They are constitutional isomers because they each contain exactly the same number and type of atoms, in this case six carbon atoms and fourteen hydrogen atoms and no other atoms.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Always be careful while placing the methyl or ethyl groups on the parent chain to calculate the numbers so that you do not repeat the same structures. Consider the part of the answer where we have considered the isomers with only 1 tertiary carbon atom. If we place the methyl group on the fourth carbon of the parent pentane chain, we will be repeating an isomer since that isomer and 2-methylpentane would be the same.
