Question
Question: The number of s-s bonds in polythionic acid \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{n}}}{{\text{...
The number of s-s bonds in polythionic acid H2SnO6 ?
A. n
B. n - 1
C. n - 2
D. None of these
Solution
Polythionic acid is an oxoacid which has a straight chain of sulfur atoms and has the chemical formula Sn(SO3H)2 (n > 2). Trithionic acid H2S3O6 , tetrathionic acid H2S4O6 are simple examples. They are the conjugate acids of polythionates. Dithionic acid H2S2O6 does not belong to the polythionic acids due to strongly different properties.
Complete step by step solution:
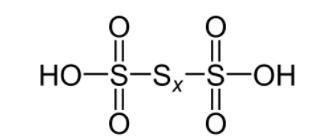
The number of s - s bonds in polythionic acid H2SnO6 are n - 1
As we can see from the diagram, number of s - s bonds in polythionic acid is equal to n - 1
**Hence, option “B” is correct
Additional Information**
Any of a series of unstable acids containing a short chain of sulphur atoms, and having the general formula H2SnO6 where n is 2, 3, 4, or more are named as "dithionic", "trithionic", "tetrathionic", "pentathionic" acid respectively.
Note:
1. All polythionates anion contains chains of sulfur atoms attached to the terminal SO3H -groups. Names of polythionic acids are determined by the number of atoms in the chain of sulfur atoms:
2. Polythionic acids with a small number of sulfur atoms in the chain n = 3, 4, 5, 6 are the most stable. Polythionic acids are stable only in aqueous solutions, and are rapidly destroyed at higher concentrations with the release of sulfur, sulfur dioxide and - sometimes - sulfuric acid.
