Question
Question: The number of covalent bonds present in \({\text{Ca}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\) is/are: (A) \({\tex...
The number of covalent bonds present in CaC2 is/are:
(A) 4
(B) 3
(C) 2
(D) 1
Solution
In a compound we have many types of bonds so we will draw structure first so that we can predict the type of bonding between them. When we predict the type of bonding between them then we can know the number of bonds as well.we also know that covalent bond formed due to electron sharing between 2 atoms
Complete step by step answer:
First we see the structure of the molecule
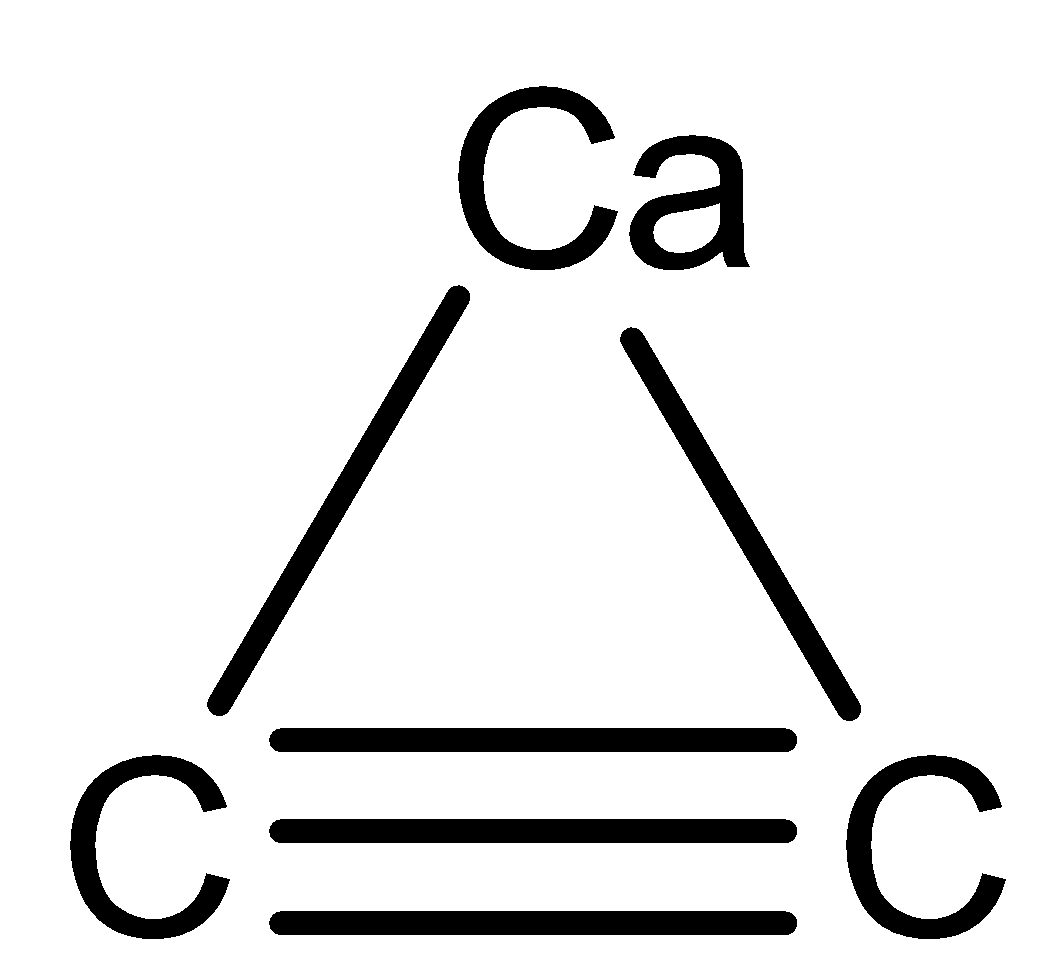
when we made CaC2 dissociate we see the ions which will tell us the number of ionic bonds present
CaC2 → Ca2 + + C22 -
Now Cadon’t have any covalent bond between them or the carbon so now we will move on to C22 - as to how many bonds it have.
Now when we study double bond or triple bond, we study about σ and π bonds
In a double bond we have 1σ and 2 π present between two carbons.
In a triple bond we have 1σ and 2 π present between two carbons.
The 1σ and 2 π bonds both are covalent bonds. So, on seeing the structure of carbon carbide above we can see there are two types of bonds present in it. One is an ionic bond and other is a covalent bond.
In covalent we have 1σ and 2 π which sums upto 3 covalent bonds.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: The formation of σ bond is the result of the head-on overlapping of the overlapping while the formation of π is the result of the lateral overlapping of the orbitals which are perpendicular to the head-on overlapping.
Ionic bond is present between ions which have charge on them while covalent bond is sharing bond in which there is no charge involved and between non-charged moieties.
