Question
Question: The number of \[{{1}^{o}}\], \[{{2}^{o}}\], and \[{{3}^{o}}\] H atoms in 2,5,6 – trimethyl octane, r...
The number of 1o, 2o, and 3o H atoms in 2,5,6 – trimethyl octane, respectively, is
(A) 16,5,3
(B) 15,6,3
(C) 16,6,3
(D) 15,5,2
Solution
The primary hydrogen atom is the atom which is attached to only one carbon atom. Generally the group attached to the primary hydrogen will be methyl group.
The secondary hydrogen atom is the atom which is attached to two other carbon atoms. The group attached to secondary hydrogen will be CH2 group
The tertiary hydrogen atom is the atom which is attached to three other carbon atoms. The group attached to tertiary hydrogen will be the CH group.
Complete step by step solution:
In the 2,5,6 trimethyl octane the methyl group is attached to 2,5,6 positioned carbon atoms.
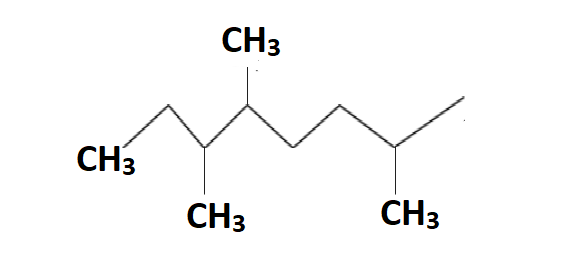
In the above structure of 2,5,6 trimethyl octane we can see the methyl groups, hydrogen groups position and carbon atoms clearly.
So by the definition of primary hydrogen atom, in this structure we can see 15 hydrogen atoms which are attached to only one carbon atom which is the hydrogen attached to the methyl group.
So by the definition of secondary hydrogen atom, in this structure we can see 6 hydrogen atoms which are attached to two carbon atoms which are the hydrogen attached to CH2 group.
So by the definition of tertiary hydrogen atom, in this structure we can see 3 hydrogen atoms which are attached to three carbon atoms which are the hydrogen attached to the CH group.
Hence, the correct option for this question is option (B).
Note: Students should know the structure of all the organic compounds. Students should make the structure of the compounds to gain marks. Do write all the definitions of all primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen atoms to show the teacher that your concept is clear. In this structure we have started the counting of carbon atoms from right, but in other questions of such type you need to start the counting from functional groups only to get the correct number of hydrogen atoms. The different functional groups are alcohols, halogens , aldehydes, nitrates,etc.
