Question
Question: The nature of X-rays spectrum is (A) Continuous (B) Line (C) Continuous and line (D) None of...
The nature of X-rays spectrum is
(A) Continuous
(B) Line
(C) Continuous and line
(D) None of these
Solution
For answering this question, we need to recall the experiment of the generation of the X-rays inside a vacuum tube. We have to analyse the interactions taking place between the electrons and the target atom. The type of the interaction will decide the nature of the X-rays spectrum, linear or continuous.
Complete step by step solution:
The electrons are subjected to an accelerating potential which gives the electrons high energy. These high energy electrons are made to interact with the target atom in an X-ray tube. The electrons get penetrated inside the X-ray tube due to this high energy. There is Coulomb’s interaction for each electron to the corresponding target atom. This interaction makes the electrons lose their energy. When they lose their energy, two kinds of X-rays are produced
(i) When the electrons lose their entire energy in a single interaction, the X-rays of continuous spectrum are generated. In this case the attacking electrons are scattered elastically by the target atom. So the electrons get decelerated and as we know that when a charged particle accelerates, it emits radiation. So, it emits a continuous X-ray spectrum.
(ii) It also happens that the attacking electrons knock out the inner shell electrons from the target atom, thereby creating a vacancy. The atom rearranges its electronic configuration to fill this vacancy. For this, an electron inside the atom makes a transition from the higher energy level to the lower energy level. Thus, the characteristic X-rays are emitted which have a linear spectrum.
Hence, the correct answer is option C, continuous and line.
Note:
We can answer this question by directly looking at the graph of the intensity variation of the X-rays with the wavelength.
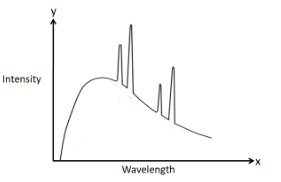
As we can clearly see in the graph, there exists a continuous region which represents the continuous spectrum and also there exists discrete lines which represent the characteristic spectrum.
