Question
Question: The most stable Carbanion is ___________ A.\(PhC{H_2}\mathop C\limits^ - {H_2}\) B. \(Ph\mathop ...
The most stable Carbanion is ___________
A.PhCH2C−H2
B. PhC−H2
C.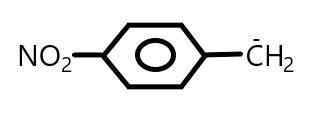
D.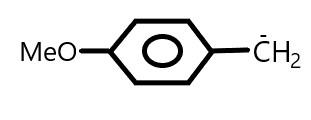
Solution
As we know that a Carbanion is basically an electron rich species which possess a complete octet. We also know that NO2 is an electron withdrawing group and presence of an electron withdrawing group stabilizes the carbanion.
Complete step by step answer:
Carbanion is the carbon atom having negative charge present on it. An electron withdrawing group increases the stability of carbanion. Resonance is another factor by which stability of carbanion increases. Now talking about the stability order of carbanion is: 1∘>2∘>3∘.
As we all know that methyl group has a +I effect which increases the intensity of negative charge on central carbon of 3∘ carbanion which further makes it unstable.
So let us analyze the above given options:
In Option (A), the carbocation present is a primary carbocation so the chances of its stability is high.
In Option (B), the carbocation is 1∘ and the presence of the phenyl group also stabilizes the carbanion.
In Option (C), the carbocation 1∘ and there is also −NO2 group which shows both −M and −I effect. As we know that the electron withdrawing group increases the stability of carbanion and stabilizes the negative charge.
In Option (D), C−is 1∘ but at the para position of phenyl group −OCH3 group is present which shows +I effect. And as we know the group that shows +I effect generally decreases the stability of carbanion. So, we can say that it will destabilize the negative charge present on the carbon atom.
So, we can conclude that OPTION (C) is the right answer. Due to the presence of electron withdrawing −NO2 group which increases the stability of carbanion.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Always remember the order of stability of carbanion where primary carbocations are most stable followed by the secondary and tertiary and the factors by which its stability is attained i.e. resonance effect, inductive effect and degree of the central carbon atom having negative charge.
