Question
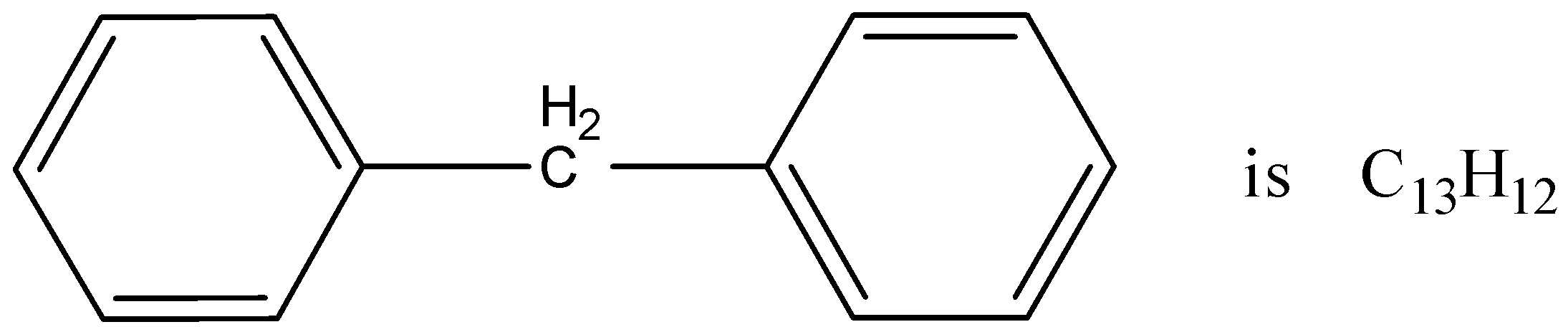
Question: The molecular formula of diphenylmethane is \({C_{13}}{H_{12}}\). How many structural isomers are po...
The molecular formula of diphenylmethane is C13H12. How many structural isomers are possible when one of the hydrogens is replaced by a chlorine atom?
A. 8
B. 7
C. 6
D. 4
Solution
There are carbon molecules which can form structural isomers because of the presence of the different residues associated with the main structures or the functional groups in the compound. Here any of the H can be replaced which means all the isomers are going to be positional isomers of Cl. Since there are two benzene rings the position in each of the benzene getting replaced replicates the chemical nature of similar isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
The molecular formula of the chemical molecule that is given here is C13H12 and the chemical structure is known diphenylmethane. This chemical compound is known as diphenylmethane as there is a methyl residue in the middle and there are two benzene ring structures associated with the central carbon atom. If one of the H residue is replaced by Cl residue from the whole diphenyl methane structure then there can be different structural isomers according to the position of the Cl residue inside the main structure.
The first isomer can be formed if any of the hydrogen in the central carbon of the methyl residue is replaced by chloride bond formation. There can be other three positional isomers which can be based on the positioning of the chloride residue on the benzene structure. There can be chloride at the ortho-position, para-position and meta-position. All of these positional isomers prove that there can be four possible isomers if one of the H is replaced by Cl.
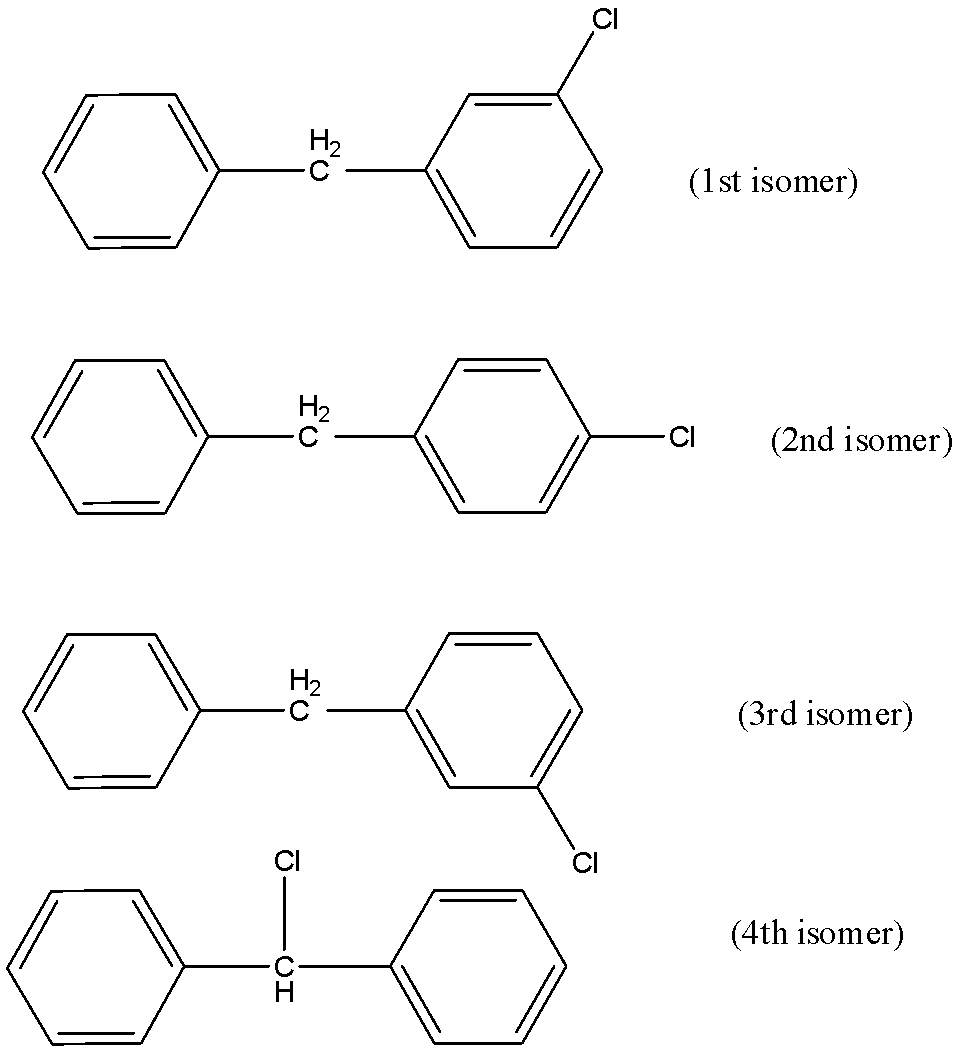
These are the 4 different positional isomers that can be produced.
Note: Different isomers can be formed based on the functional groups present. This can be based on the type of position of the specific functional group involved in the given molecule or the type of functional group present.
