Question
Question: The molecular formula of diphenyl methane is given in the figure. How many structural isomers are po...
The molecular formula of diphenyl methane is given in the figure. How many structural isomers are possible, when one of the hydrogen is replaced by a chlorine atom?
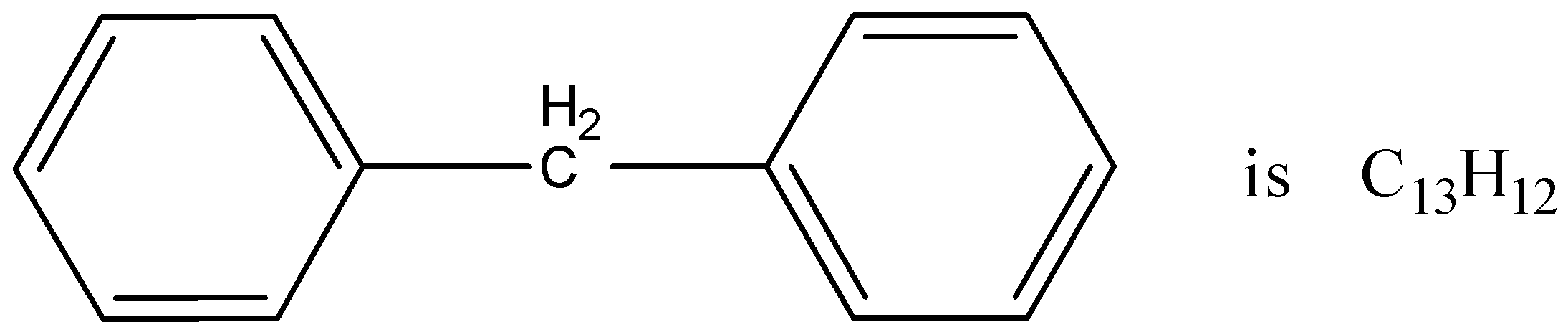
A.6
B.4
C.8
D.7
Solution
We know that isomerism is a phenomenon in which two or more compounds possess the same chemical formula but their structural arrangement is different. There are two types of isomers, structural isomers and stereoisomers.
Complete step by step answer:
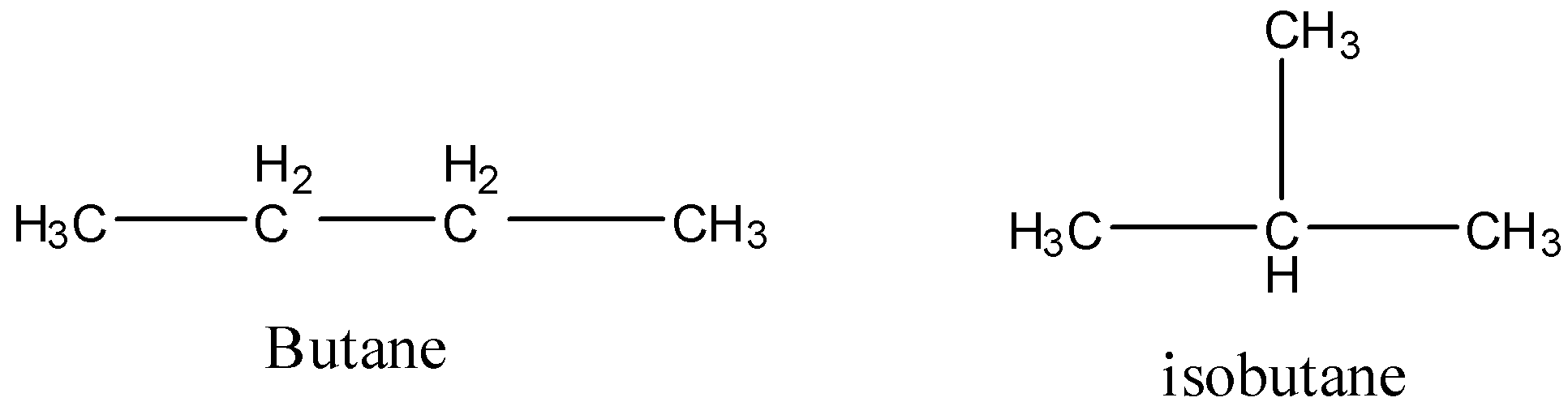
Let’s first understand structural isomers. They are those isomers that have the same molecular formula but arrangement of atoms is different. Let’s take the example of butane and isobutene. Both have same molecular formula that is, C4H10 but arrangement of atoms in both the compounds are different.
Now, come to the question. The given compound is diphenyl methane.
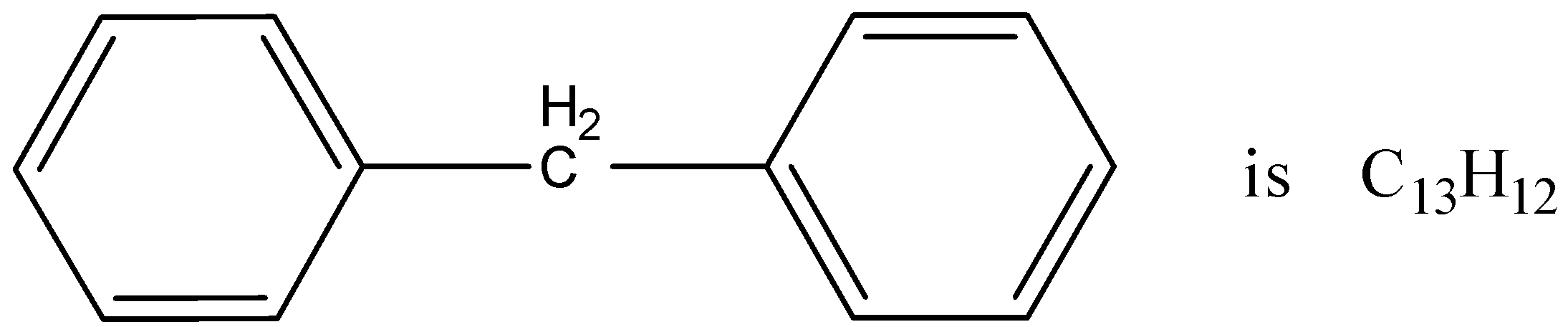
We have to identify the number of structural isomers on replacing one hydrogen atom by a chlorine atom.
Now, identify the carbon atoms on which replacement is possible.
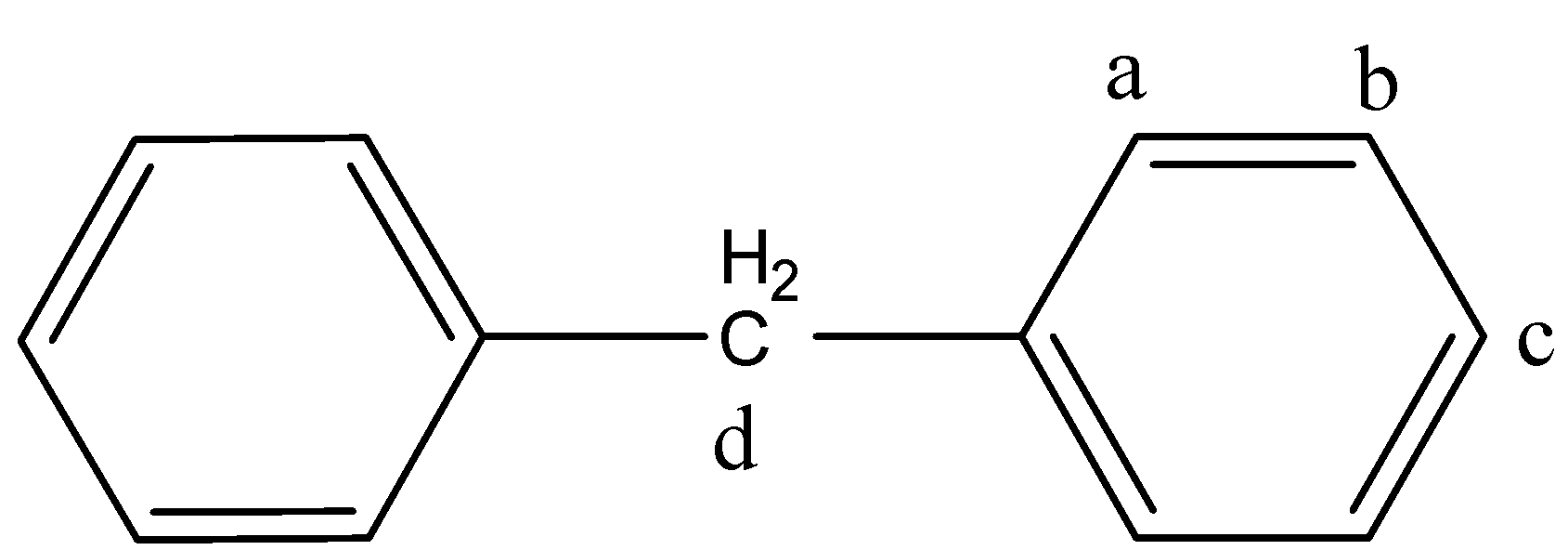
On the carbon atoms (a, b, c and D) replacement is possible. On all other carbon atoms, replacement is the same as that of a or b or c or D.
Now, draw all isomers by replacing one hydrogen atom.
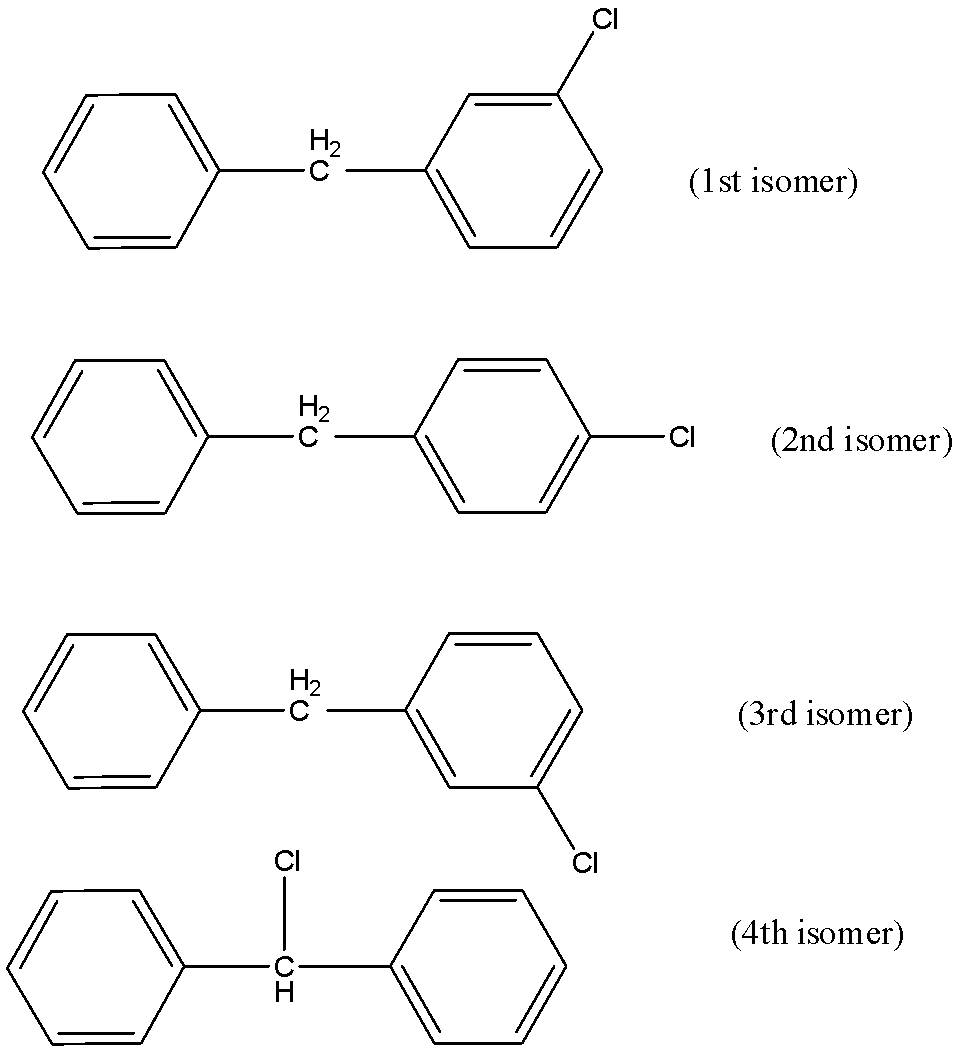
So, we get to know that four isomers are present when one hydrogen atom is replaced by chlorine atom.
So, the correct answer is Option B .
Additional Information:
Structural isomerism is classified into different types, such as, chain isomerism, position isomerism, functional isomerism etc.
Position isomerism is the phenomenon in which isomers differ with respect to the position of the multiple bonds, substituents or functional groups.

Note:
Stereoisomerism is the phenomenon in which compounds possess the same structural formula and molecular formula but their atomic arrangement in space is different. The isomers are known as stereoisomers. The three types of Stereoisomers are geometrical isomerism, optical isomerism and conformational isomerism
