Question
Question: The mirror image of the curve \[\arg \left( {\dfrac{{z + i}}{{z - 1}}} \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{4},i =...
The mirror image of the curve arg(z−1z+i)=4π,i=−1 in the line x−y=0 is
A.arg(z+1z+i)=4π
B.arg(z−iz+1)=4π
C.arg(z+1z−i)=4π
D.arg(z−1z+i)=4π
Solution
First of all find the locus represented by the curve. And then we will find the mirror image along the given line. We know that a complex number is z=x+iy using this find the locus.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that,
arg(z−1z+i) but a complex number is written as z=x+iy.
So write the curve given above in complex number form as
⇒z−1z+i=x+iy−1x+iy+i
Taking i common in numerator, and writing real and imaginary part as in complex number
⇒(x−1)+iyx+(y+1)i
Now to simplify the terms we will multiply numerator and denominator by (x−1)−iy
⇒(x−1)+iyx+(y+1)i×(x−1)−iy(x−1)−iy
Now multiply the terms in numerator and denominator will be a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)
⇒(x−1)2−(iy)2x(x−1)−xyi+(y+1)(x−1)i−(y+1)yi2
Since i2=−1 second term of denominator changes to
⇒(x−1)2+y2x(x−1)−xyi+(y+1)(x−1)i+(y+1)y
Multiplying the terms in numerators and separating the real and imaginary parts
⇒(x−1)2+y2x2−x+y2+y+i(xy−y+x−1)−xy)
The terms xy cancels here and we get
⇒(x−1)2+y2x2−x+y2+y+i(x−y−1)
Now here we separated the real and imaginary terms.
Given that
arg(z−1z+i)=4π
In this case real and imaginary parts are the same. So equating them,
⇒(x−1)2+y2x2−x+y2+y=(x−1)2+y2(x−y−1)
Cancelling the denominators from both the sides
⇒x2−x+y2+y=x−y−1
⇒x2−x+y2+y−x+y+1=0
Adding x and y terms,
⇒x2+y2−2x+2y+1=0
Now if we observe this is the locus of a circle with center (1,−1).
It can be plotted as ,
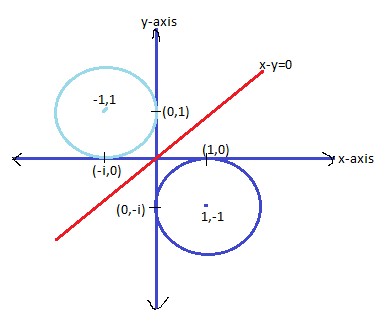
Now since the locus of light blue circle is the mirror image of the curve. Thus the curve is given as
arg(z+1z−i)=4π.
Hence option C is the correct answer.
Note: Students generally make mistakes when we simplify the fraction with the help of complex conjugate of term in denominator. So take the simplification term carefully. And the mirror image of the curve is along the line x=y so draw that line to get an exact idea of the mirror locus.
