Question
Question: The minimum value of the expression cos2x+cosx for real values of x is: [a] \(\dfrac{-9}{8}\) [b...
The minimum value of the expression cos2x+cosx for real values of x is:
[a] 8−9
[b] 0
[c] -2
[d] None of these
Solution
Hint: Checking for critical points in the intervale [0,2π) is sufficient due to periodicity of cos x and cos2x. Differentiate once w.r.t x and put derivative equal to 0 to find the critical points. Use the first derivative test to determine whether a critical point is local maxima or minima.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First derivative test: If f(x) is a continuous and differentiable function and f’(a) = 0, then
[i] If x→a−limf′(x)>0 and x→a+limf′(x)<0, then x = a is a point of local maxima
[ii] If x→a−limf′(x)<0 and x→a+limf′(x)>0, then x = a is a point of local minima
Let f(x) = cos2x+cosx
Differentiating once we get
f’(x) = -2sin2x-sinx = 0
i.e. 2sin2x+sinx = 0
We know that sin2x = 2sinx cosx
Using the above formula, we get
4sinxcosx+sinx = 0
Taking sinx common, we get
sinx(4cosx+1)=0
i.e sinx = 0 or 4cosx + 1 = 0
if sinx = 0 then x=0,π{Because sinx = 0 when x=nπ }
if 4cosx +1 = 0 then
cosx=4−1⇒x=π+arccos(41),π−arccos(41)
In finding the above roots, we have used the property cos(arccosx)=x and cos(π−θ)=cos(π+θ)=−cosθ.
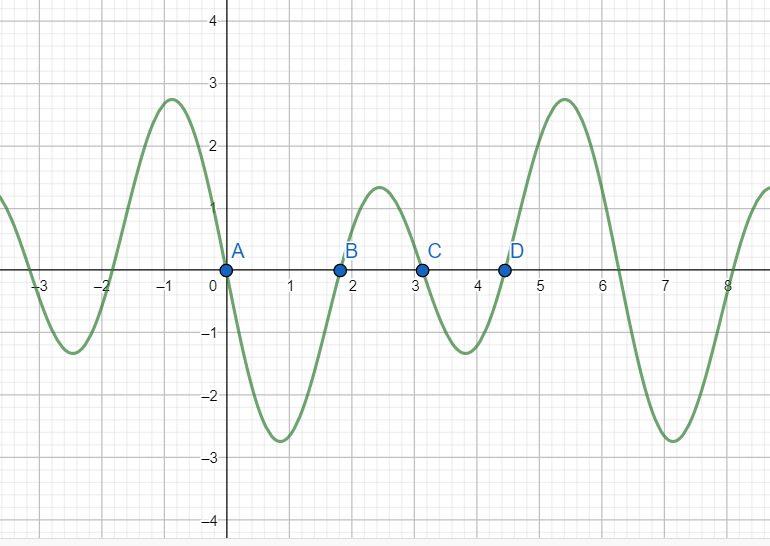
The graph of f’(x) is shown above.
Around point x = 0(Point A in the graph of f’(x)): f’(x) changes sign from +ve to -ve as we move left of 0 to right of 0. Hence, from first derivative test, x = 0 is a point of local maxima
Around point x=π−arccos(41)(Point B in the graph of f’(x)): f’(x) changes sign from -ve to +ve as we move left of π−arccos(41) to the right of π−arccos(41). Hence, from the first derivative test, x=π−arccos(41) is a point of local minima.
Around point x=π (Point C in the graph of f’(x)): f’(x) changes sign from +ve to -ve as we move left of π to the right of π.
Around point x=π+arccos(41) (Point D in the graph of f(x)): f’(x) changes sign from -ve to +ve as we move left of π+arccos(41) to the right of π+arccos(41). Hence x=π+arccos(41) is a point of local minima.
Now
f(π−arccos(41))=cos(2π−2arccos(41))+cos(π−arccos(41))=cos(2arccos(41))−cos(arccos(41))=2cos2(arccos(41))−1−41=162−45=8−9
and
f(π+arccos(41))=cos(2π+2arccos(41))+cos(π+arccos(41))=cos(2arccos(41))−cos(arccos(41))=2cos2(arccos(41))−1−41=162−45=8−9
Hence the minimum value of the trigonometric expression cos2x+cosx is 8−9.
Hence option [a] is correct.
Note: Alternative solution:
We know cos2x=2cos2x−1
Hence cos2x+cosx=2cos2x−1+cosx
Put t=cosx we getf(t)=2t2+t−1,−1≤t≤1
We know the quadratic expression ax2+bx+c where a>0 attains minima when x=2a−b
Since 2a−b=2×2−1=4−1 is in the domain of t.
We have the minimum value of f(x) = minimum value of f(t)
=2(4−1)2+4−1−1=81−45=8−9
which is the same as obtained above.
