Question
Question: The majority carriers in a p-type semiconductor are. A. Electrons. B. Holes. C. Both A and B. ...
The majority carriers in a p-type semiconductor are.
A. Electrons.
B. Holes.
C. Both A and B.
D. impurities.
Solution
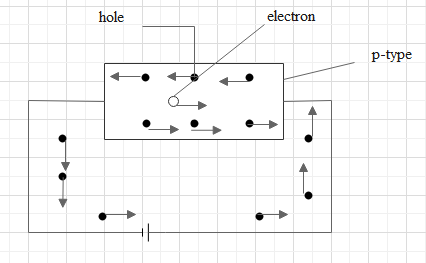
We know that the semiconductors doped with the acceptor type impurities are called p-type semiconductors. The acceptor is defined as trivalent impurity because it creates a hole which can accept an electron from neighbouring bonds.
Complete answer:
We can see that as trivalent impurity because it creates a hole which can accept an electron from a neighbouring bond. Obviously, there are holes created by the acceptor atoms which are thermally generated while electrons are only due to the thermal generation.
Firstly, Group IV elements: Si, Ge etc are referred to as Intrinsic semiconductors.
We know group IV elements form covalent bonds. So if we replace one among the atoms with a group III element (B, Ga etc). We know that it will form 3 covalent bonds with 3 neighbouring group IV elements and therefore the fourth neighbour isn't ready to form a bond as there's a vacancy of an electron which we call hole. Thus making a charged hole to travel within the network (lattice). These sort of semiconductors are semiconductor devices thanks to the presence of mobile charge (Though holes don't move instead electrons fill the opening by leaving their site thus transferring holes there).
Important thing to notice is despite the charged hole, the semiconductor is electrically neutral as all the constituents are electrically neutral.
Hence holes are the majority charge carriers and electrons are minority charge carriers.
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Additional Information:
The process of the addition of desirable impurity to a pure semiconductor to increase its conductivity is called doping. The impurity added is called dopant and the semiconductor doped with the impurity is known as extrinsic or doped semiconductors.
The semiconductor obtained by doping trivalent impurity with the pentavalent impurities. When a pentavalent impurity atom substitutes the tetravalent atom. It uses four of five valence electrons in forming four covalent bonds with neighboring atoms while the 5th electron is loosely bound to impurities. As each pentavalent atom donates one electron for conduction it is known as a donor. These semiconductors have free electrons donated by the donors and generated by the thermal process while the holes are only due to thermal generation. In n-type electrons are the majority charge carriers and electrons are the minority charge carriers.
Note:
The semiconductors doped with acceptor type impurities are called p-type semiconductors because most of the current in these semiconductors are carried by the holes which have an effective positive charge. Doping does not change the overall neutrality of semiconductors.
