Question
Question: The major product of the following reaction is:  LiAlH4
LiAlH4
A. CH3CH2CH2CHO
B. 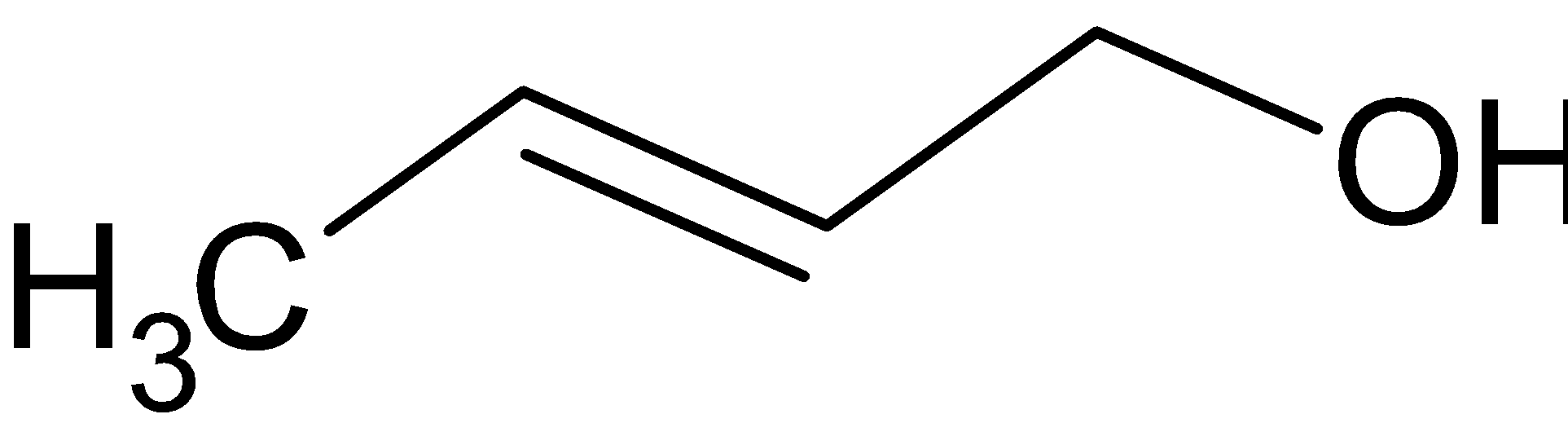
C. 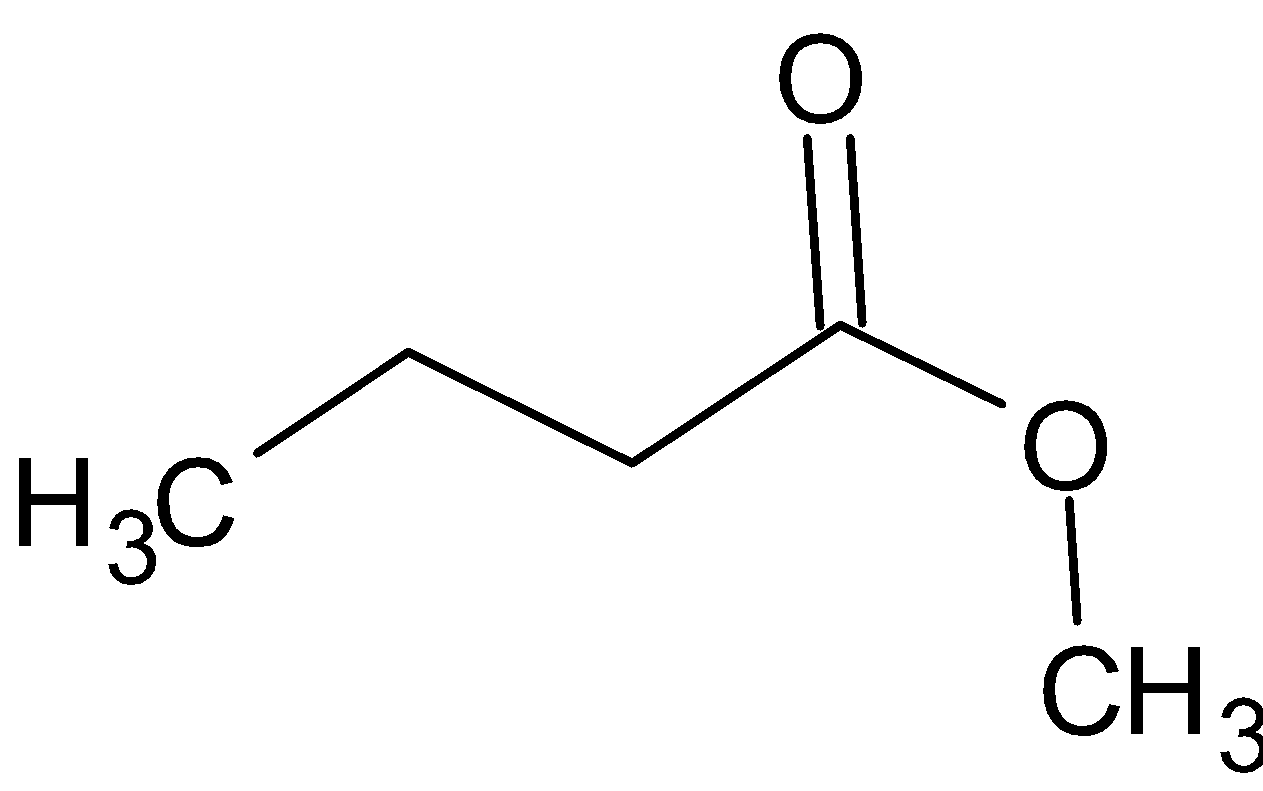
D. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
Solution
LiAlH4 is a very strong reducing agent. It reduces carbonyl, carboxylic acid and ester. It also reduces nitrile, amide and aryl nitro group to amine. Reduction is the exchange of electrons in association with hydrogen and oxygen or some other atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Esters are the carboxylic acid derivatives in which the hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkoxy group. They are the chemical organic compounds which are formed when an alcohol reacts with a carboxylic acid. It has the molecular formula RCOOR.
Lithium aluminium hydride is a very strong hydride (H−). It can reduce carboxylic acids, esters, aldehydes and ketones.
Both reduction and hydrolysis of esters produces alcohol. But reduction of esters using LiAlH4 produces two alcohols while hydrolysis of esters produces an alcohol and an acid.
Generally primary alcohols are produced by reducing esters. The mechanism involves the nucleophilic attack by the hydride, leaving group removal, nucleophilic attack by hydride anion and the protonation of alkoxide. Thus alcohol is formed.
When the given compound is reacted with LiAlH4, it produces two alcohols. One alcohol is produced from the alcohol portion of ester and the other alcohol is produced from the reduction of carboxylate portion.
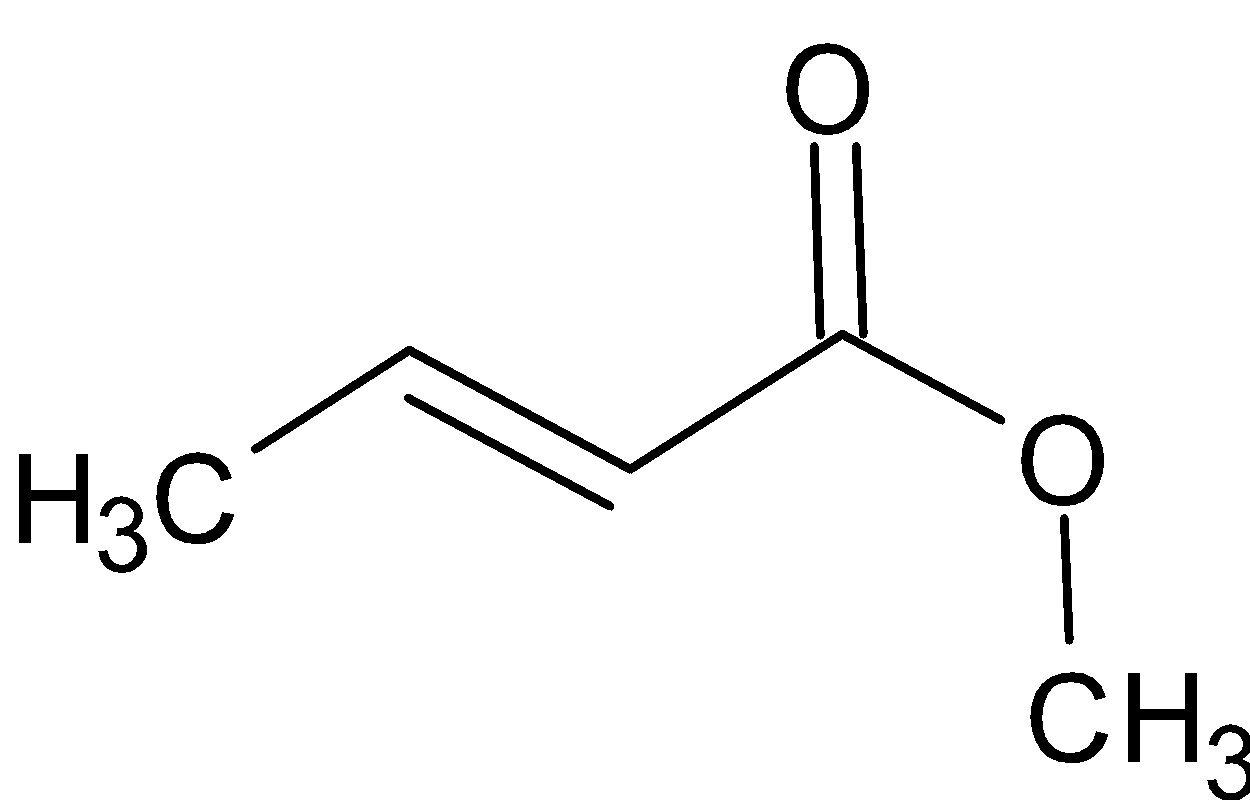 LiAlH4
LiAlH4 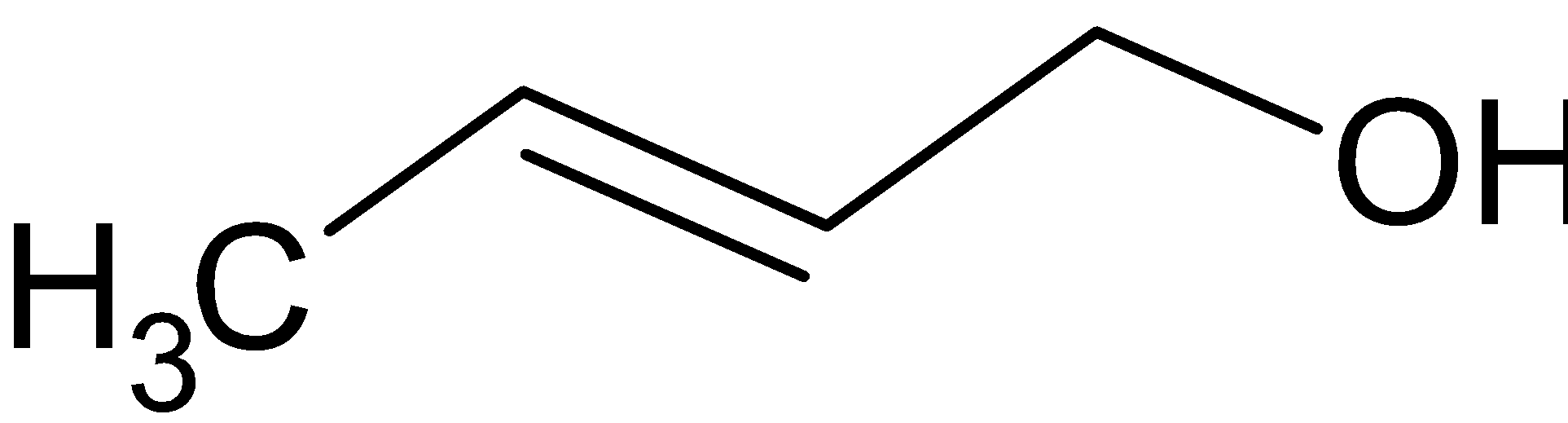
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note:
This type of reaction occurs in two steps- nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction and nucleophilic addition reaction. LiAlH4 is more reactive than NaBH4. Therefore NaBH4 cannot be used for reducing the acids or esters. NaBH4 can reduce aldehydes, ketones and acid halides to alcohols. Reduction of esters using NaBH4 is a slow process. LiAlH4 can reduce ketones to secondary alcohols.
