Question
Question: The major product obtained on interaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide is: (...
The major product obtained on interaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide is:
(A) Benzoic acid
(B) Salicylaldehyde
(C) Salicylic acid
(D) Phthalic acid
Solution
The interaction of phenol with hydroxide and carbon dioxide gives the acid group attached to the phenol ring.
Complete step by step solution:
The reaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide is Kolbe’s Schmidt reaction. So, let us see what is the mechanism for the given reaction.
Kolbe’s Schmidt reaction- It is also known as Kolbe process. This process in short is all about the carboxylation chemical reaction which takes place in presence of sodium salts heated with carbon dioxide under pressure. The pressure for the process is about 100 atm and the temperature is 125∘C. The product is then treated with the sulphuric acid giving the final product as aromatic hydroxy acid i.e. salicylic acid.
Mechanism- The Kolbe’s Schmidt reaction proceeds in a way that gives nucleophilic addition of sodium phenoxide to carbon dioxide which finally gives salicylate.
-Finally, salicylate reacts with acid to form salicylic acid by acidification.
Reaction-
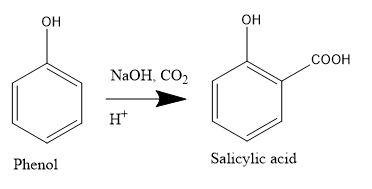
Therefore, option (C) is correct.
Additional information:
-Kolbe’s Schmidt reaction is named after Hermann Kolbe and Rudolf Schmidt. It is an additional reaction. The product of the specified reaction is salicylic acid which is the precursor of aspirin.
-Kolbe’s reaction can also be used in converting sodium acetate to ethane.
-True aromatic acids do not undergo Kolbe’s electrolytic reaction.
-Kolbe’s synthesis is the same as Kolbe’s reaction or Kolbe’s electrolysis.
Note: As from the hint itself, we came to know that there will be formation of acid substituted phenol. Thus, option (B) salicylaldehyde must not be considered from very prior beginning.
