Question
Question: The major product obtained in the following reaction is: 
A. C6H5CH=CHC6H5
B. (−)C6H5CH(OtBu)CH2C6H5
C. (+)C6H5CH(OtBu)CH2C6H5
D. (±)C6H5CH(OtBu)CH2C6H5
Solution
We know that potassium tert-butoxide is a non-nucleophilic base. It is also very bulky in size. Due to which it helps in the elimination reaction. Here, the mechanism involves E-2 mechanism.
Complete step-by-step answer: It is known to us that the nucleophile can act as a base and abstract acidic hydrogen and nucleophilic substitution reactions will take place. This depends upon the strength of the nucleophile. If the nucleophile is poor, then elimination will take place, on the other hand, if it is strong in nucleophilic strength then its substitution reaction will take.
In this elimination reaction, the alkene formed which is more substituted is found to be more stable in nature. This is in accordance with the Zaitsev product.
The mechanism of the reaction takes place as follows-
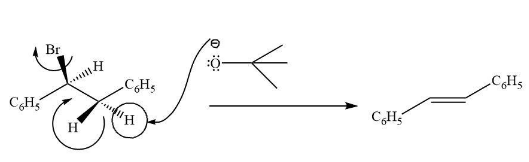
This tertiary butoxide ion first takes alpha hydrogen to the carbon containing halogen group. This hydrogen is present in antiperiplanar plane i.e. it is present in the plane opposite to the halogen group. Due to which there is a formation of double bond in the molecule.
Hence, option (A) C6H5CH=CHC6H5, is the correct option.
Note: The role of nucleophile as elimination and substitution also depends upon its size. If it is bulky in nature, then it acts as a base. And if it is small in size then substitution will take place.
