Question
Question: The major product obtained in the following reaction is: 
(A) 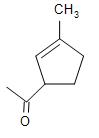
(B) 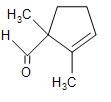
(C) 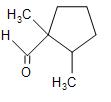
(D) 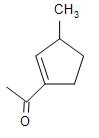
Solution
The base causes the abstraction of the proton, and there are two carbonyl groups present which will undergo aldol condensation reaction within the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given compound, there is a presence of two carbonyl groups at both the ends. That is, an aldehyde and a ketone. Both the carbonyl groups have hydrogens on the α- carbon adjacent to it.
So, in presence of the strong base of sodium hydroxide, it undergoes the intramolecular cross aldol condensation as follows:
- The hydroxide ion of the base deprotonates the carbonyl group, abstracting the more acidic α- hydrogen. Since, the α- hydrogen near the aldehyde group due to the presence of the methyl group over the α- carbon, increases its electron-density. Thus, making the α- hydrogen less acidic.
Whereas the methylene carbon adjacent to the ketone group, forming a secondary carbanion is more acidic. So, the sodium hydroxide base, abstracts hydrogen from the methylene carbon, forming an enolate ion.
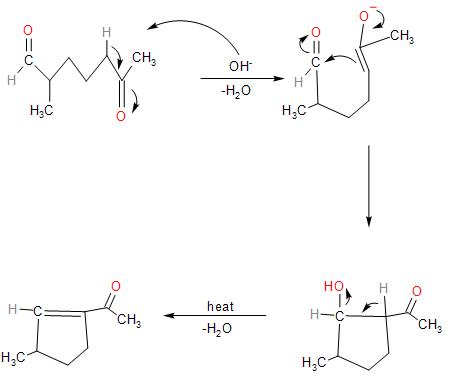
The negative charge disperses over the carbonyl group, forming a double bond and a negative charge over oxygen.
- The enolate ion attacks on the partially positive charge on the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde group. Thus, forming a 5-membered ring and a β−hydroxyketone
- On further heating, it loses a water molecule, forming an !!α!! , !!β!! - unsaturated ketone compound.
Therefore, the major product obtained in the intramolecular cross aldol condensation reaction is option (D).
Note: It is an intramolecular reaction, as both the carbonyl groups, that is the aldehyde and ketone group are present within the molecule and the cross-aldol condensation takes place. On either side of the ketone, the α- hydrogen of the methylene carbon is more acidic than the methyl group.
