Question
Question: The long hydrocarbon chain in soap is water-repelling (hydrophobic), which is called: A. polar ta...
The long hydrocarbon chain in soap is water-repelling (hydrophobic), which is called:
A. polar tail
B. ring chain
C . non-polar tail
D. none of the above
Solution
Soap can be formed by mixing sodium salt of fatty acids. If the salt is potassium salt that it would be softer. Soap can be produced by the hydrolysis of fat; this hydrolysis can be basic or acidic hydrolysis.
Complete step by step answer:
Fatty acids are a carboxylic acid of a hydrocarbon. This type of hydrocarbons is with very high carbon numbers. Fatty acids are a unit of fat or oil. The hydrocarbon of fatty acids has two parts, one is a polar part and another one is the nonpolar part. The polar part is hydrophilic .i.e. that part has affection towards water or it can be said that it is soluble in water. But the other part is hydrophobic .i.e. that part repels water or it can be said that it does not soluble in water.
In these two parts, one polar part is called the polar head. And the nonpolar part is called the tail. Also, the nonpolar part is a large chain of carbon like tail. The structure of the fatty acid is shown below.
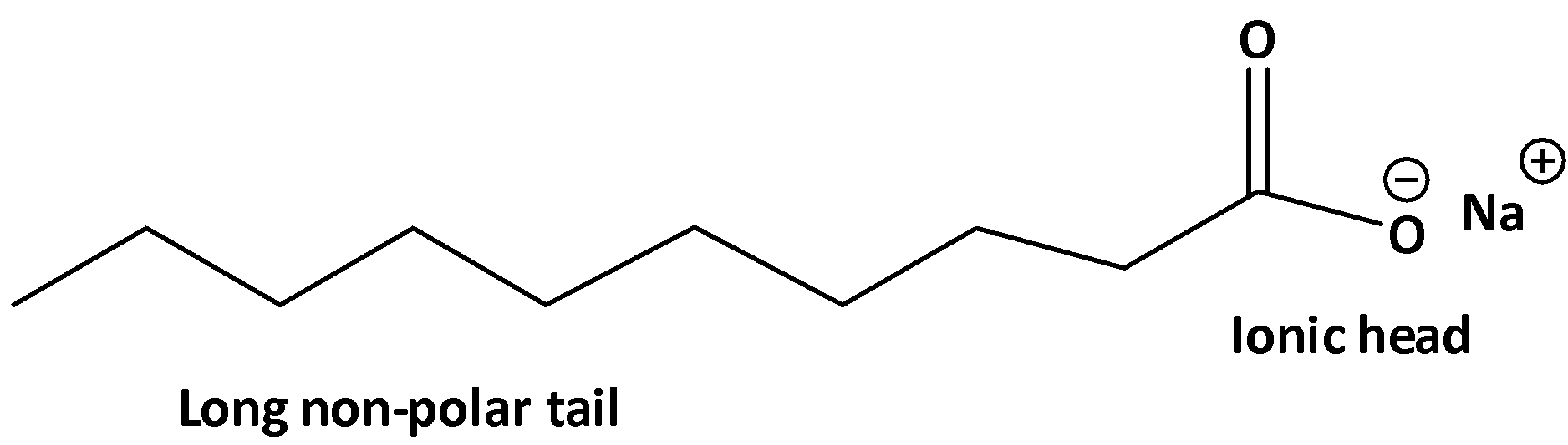
Therefore, the long hydrocarbon chain in soap is water-repelling (hydrophobic), which is called the nonpolar tail.
So, the correct option is C.
Note:
Fatty acids do not have any ring in its tail but unsaturation can be present in fatty acids. There is no polar group in the tail which can make the tail of fatty acid polar. The hydrocarbon of fatty acids has one polar hydrophilic head and one is a non-polar hydrophobic tail. The hydrogenation reaction of unsaturated fatty acids is the reaction where the hydrogen gets added in the double bond of the alkene or alkyne in presence of nickel. The nickel acts as a catalyst in solid-state. That is why this catalysis is known as a heterogeneous catalyst.
