Question
Question: The large muscular sheet which forms the floor of the chest cavity is known as a. Diaphragm b. L...
The large muscular sheet which forms the floor of the chest cavity is known as
a. Diaphragm
b. Lungs
c. Ribcage
d. None of the above
Solution
The large muscular sheet which forms the floor of the chest cavity is a C-shaped or dome-shaped (curve upwards) structure that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. This muscular sheet plays an important role during the process of respiration.
Complete answer:
Option (A) is correct. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped structure and this dome curves upwards. The superior surface of this dome forms the floor of the chest cavity and the inferior surface forms the roof of the abdominal cavity. It is the main muscle of respiration and functions in the breathing process.
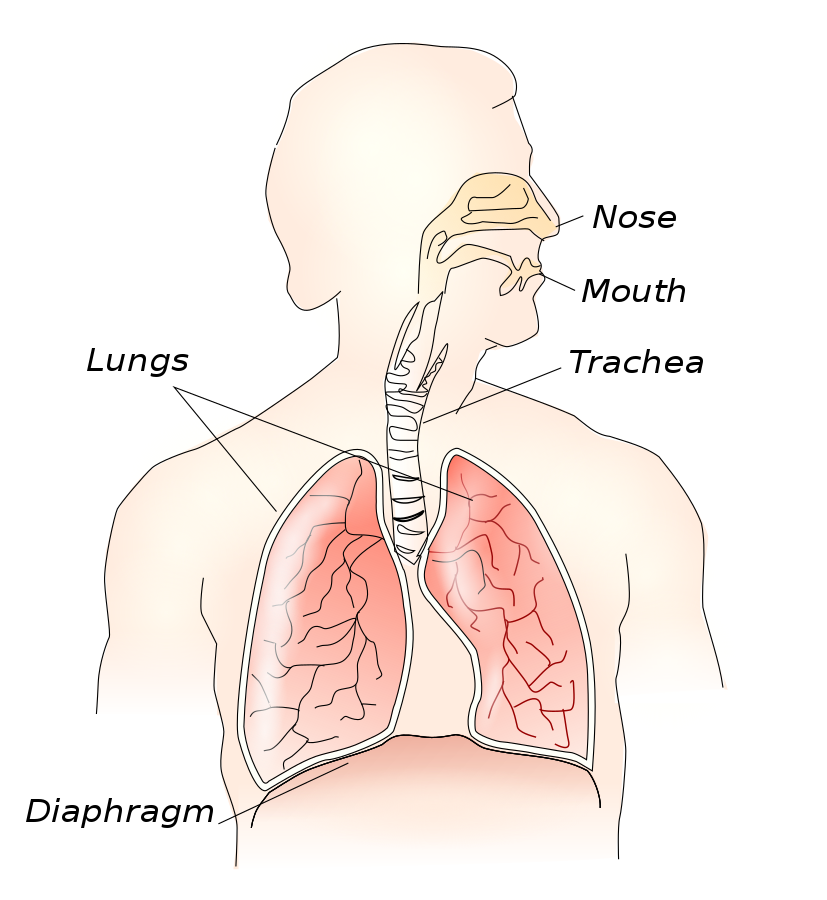
Option (B) is incorrect. Lungs are the organs of the respiratory system and they are present in a pair inside the thoracic cavity of humans. The main function of the lungs involves the exchange of gases i.e., oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the blood.
Option (C) is incorrect. The rib cage is the arrangement of 12 pairs of ribs that are attached to the vertebral column and sternum in the thoracic cavity. It helps to protect the lungs and the heart present in the thoracic cavity. It is a bony and cartilaginous structure surrounding the thoracic cavity and supporting shoulder girdle to form the core part of the human skeleton.
Option (D) is incorrect. The diaphragm is the large muscular sheet which forms the floor of the chest cavity. This implies that option (A) is correct, therefore, ‘none of the above’ option cannot be correct.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Diaphragm contracts and relaxes during inhalation and exhalation of air. Apart from serving the function in respiration, the diaphragm is also involved in non-respiratory functions such as to expel vomit, urine, and feces from the body by increasing the intra-abdominal pressure; helps in childbirth.
