Question
Question: The Kolbe’s electrolysis of potassium succinate gives \(C{O_2}\) and _____ A.Ethene B.Ethane C...
The Kolbe’s electrolysis of potassium succinate gives CO2 and _____
A.Ethene
B.Ethane
C.Methane
D.Methanol
Solution
We have to know that in Kolbe’s electrolysis, the dicarboxylic molecules undergo decarboxylation first and products alkenes are formed by dimerization. We have to know that a radical intermediate forms after decarboxylation, the intermediate gets combined, and alkene is formed as a product.
Complete answer:
We have to know that hydrocarbons which are useful substances are produced by Kolbe’s electrolysis. With the help of liquid ammonia, Kolbe electrolysis could be modified. In anode, free radicals are formed and once the free radicals are formed at anode, they go through dimerization and alkenes are formed as a product.
We can draw the structure of potassium succinate as,
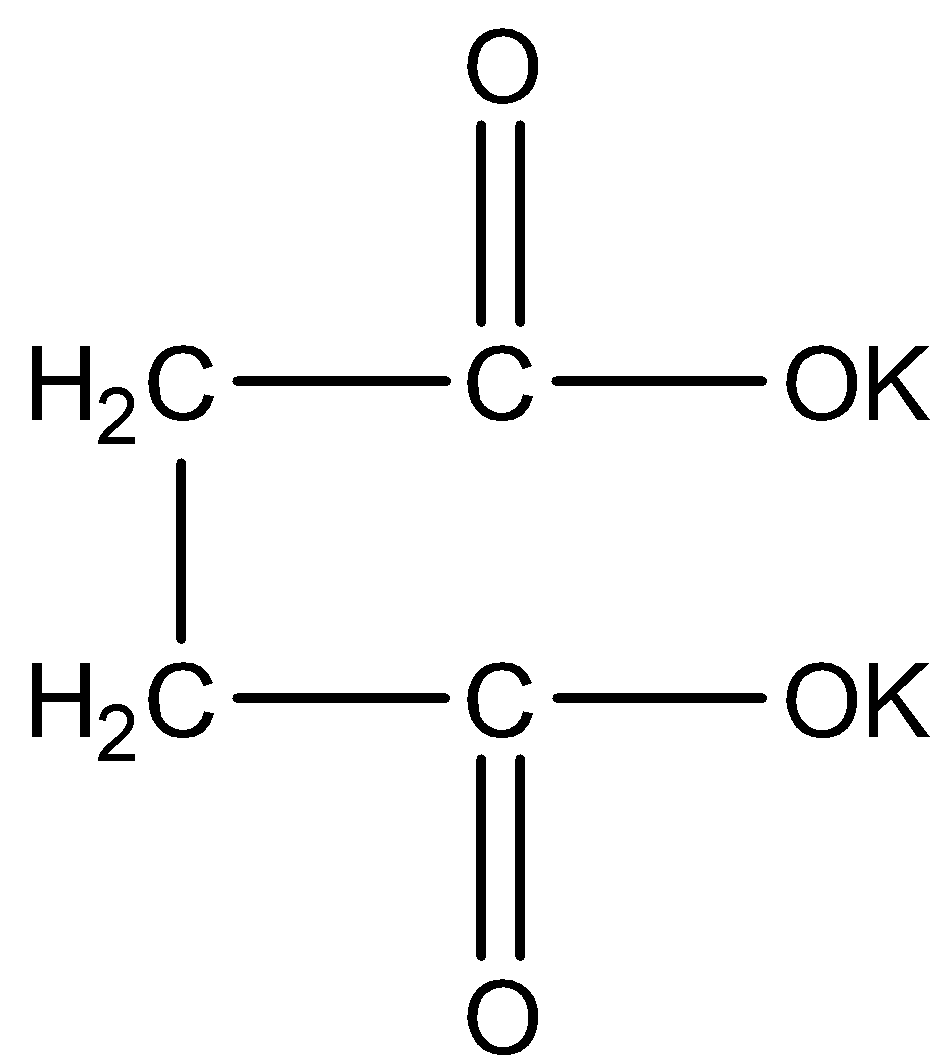
Symmetrical hydrocarbons are formed by Kolbe’s electrolysis. We can write the chemical equation for Kolbe’s electrolysis for potassium succinate as,
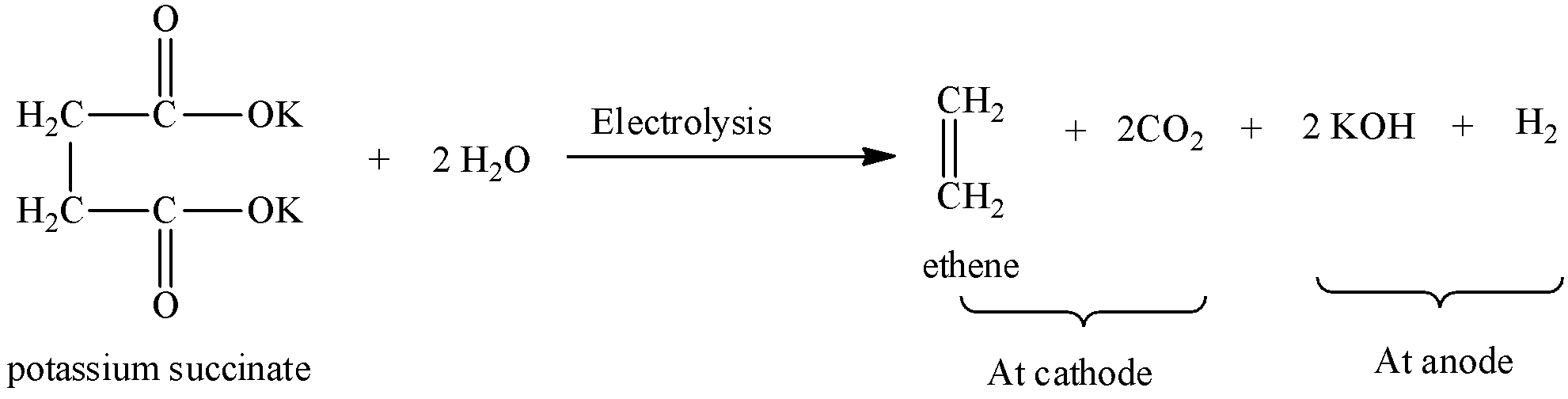
At cathode, carbon dioxide and ethene is formed by decarboxylation of potassium succinate.
At anode, potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas is formed.
So, Kolbe’s electrolysis of potassium succinate results in the formation of ethene and carbon dioxide.
Option (A) is correct.
Note:
We could use Kolbe’s electrolysis to form polymers that have low molecular weight and also polystyrene could be prepared by Kolbe’s electrolysis. We have to know that for any organic molecule that contains two carboxylic acids on side by side carbon, they are not unstable and to provide stabilization, alkenes are formed as a product. We have to know that the number of carbon dioxide molecules that are given out in Kolbe’s electrolysis is the carboxylic acid functional group found in the molecule.
