Question
Question: The IUPAC name of given compound is: 
A.3 - ethyl - 5 - methylheptane
B. 5 - ethyl - 3 - methylheptane
C. 3,5−diethylhexane
D. 1,3−diethyl−1−methylpentane
Solution
We need to know that International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is abbreviated by IUPAC. IUPAC standardizing nomenclature in chemistry, IUPAC sets rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds is one of the best known works for IUPAC. IUPAC is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations.
Complete answer:
Now we discuss about the rules of IUPAC system of nomenclature for linear compounds as follows:
First of all we see the number of chains lengths in the given compound. If the number of carbon atoms is one, then the compound is named as meth− , for two carbon atoms, then the compound is given as the name eth− , and for three, then called as prop− , etc. For numbering carbon atoms with the longest chain, the parent carbon chain forms the end which has a nearest substituent to give a minimum number to the carbon atom bearing substituent.
If the compound contains branched chains, the one which is having more substituent is preferred than the other. In a compound, there are different substituents then they are listed in alphabetical order.
Hydrocarbon chain type is saturated or unsaturated with one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) or are called −ane , −ene and −yne respectively. These are called primary suffixes. For example, methane, ethene and propyne, etc.
Then we see the functional group present in the compound.
Alcohols (−OH) : prefix: hydroxy− and suffix: −ol . For example: CH3CH2OH , name of the compound is ethanol and CH3OH , IUPAC name is methanol.
Carboxylic acid (−COOH) : prefix: carboxy- and suffix: -oic acid. For example: ethanedioic acid (COOH−COOH) .
Ketone : suffix: −one . For example: methanone H2C=O ,.
Alphabetical order is first considered before the parent hydrocarbon without considering the presence of a functional group.
Carbon atoms contain a functional group itself (e.g., −CHO, −COOH, etc) are linked to a carbon chain, such carbon should be also numbered.
For example,
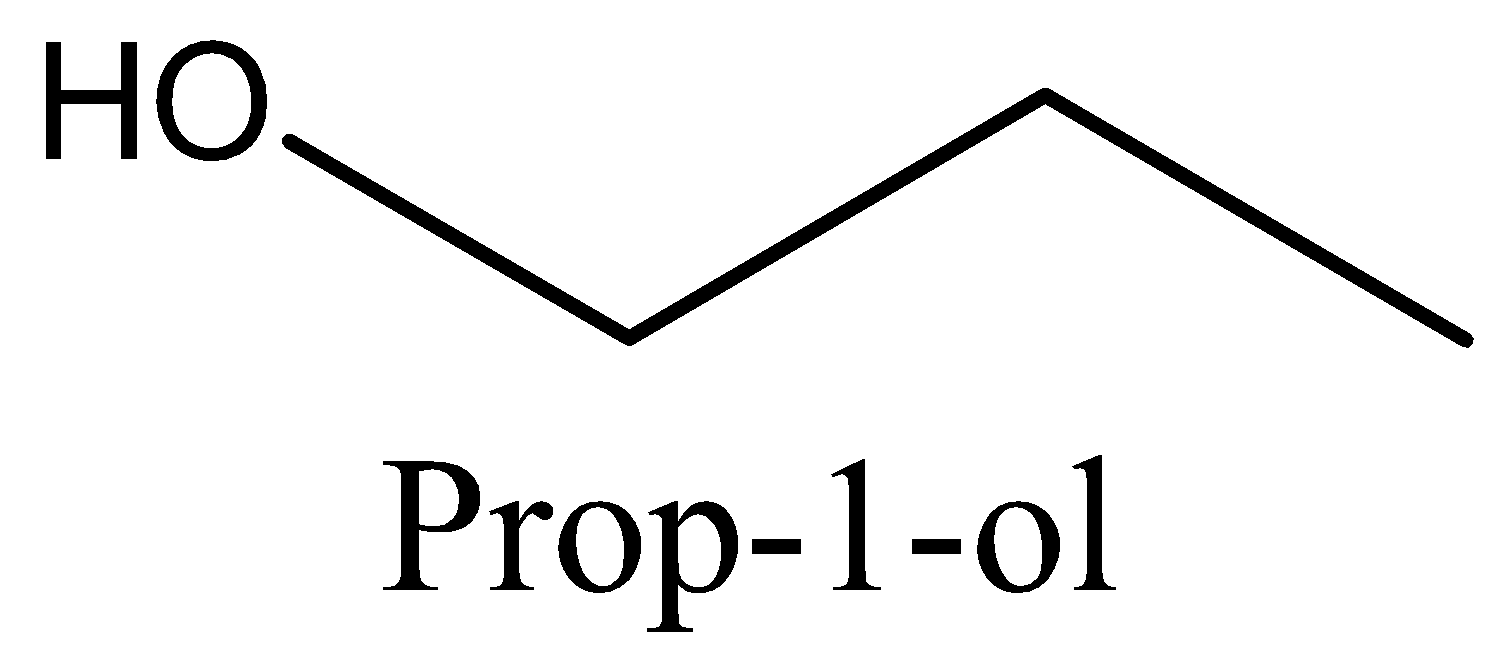
The name of the compound is prop−1−ol .
The given compound
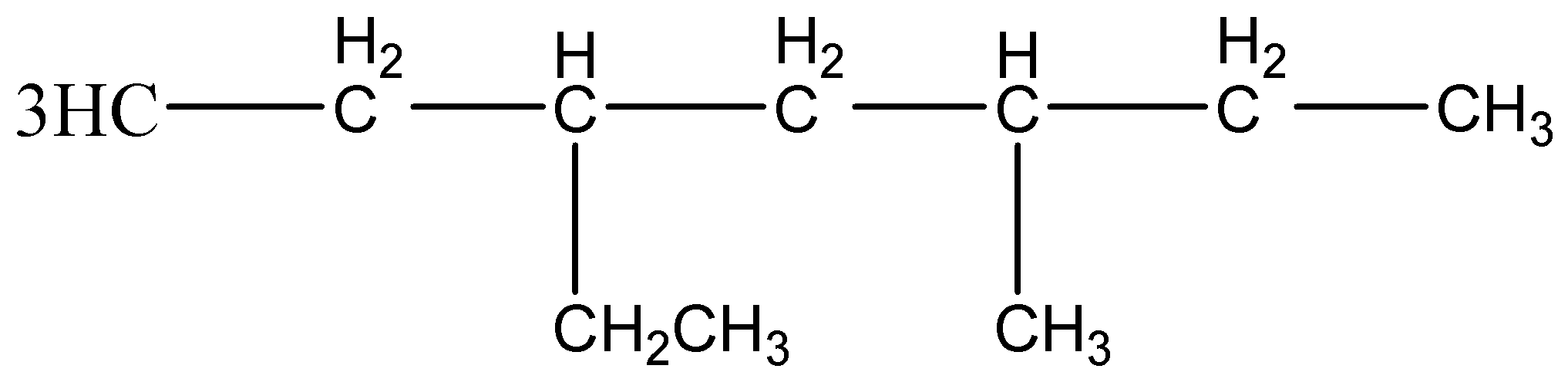
It contains seven carbons in a chain form. So, Parent compound name is heptane .
The above compound contains different substituents, so alphabetical order with their carbon number is given.
So the numbering is,
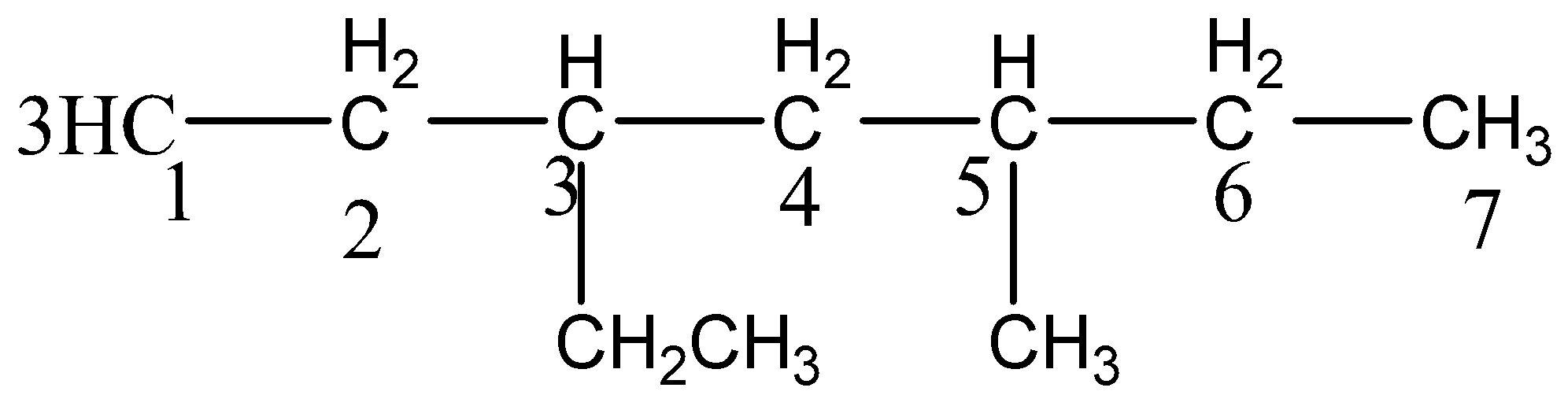
The third carbon atom contains ethyl substituent and the fifth carbon atom contains methyl substituent.
IUPAC name is 3−ethyl−5−methyl−heptane .
The correct option is A. 3 - ethyl - 5 - methylheptane .
Note:
-IUPAC gives a unique name to every chemical compound; IUPAC is a non-governmental organization. -IUPAC addresses many global issues involving the chemical sciences. In 1919 IUPAC was established and -IUPAC also published books, fields including chemistry, biology and physics. The purpose of this IUPAC system is a unique and unambiguous name to each and every structure, and to compare each name with a unique and unambiguous structure.
