Question
Question: The ion which is not tetrahedral in shape \(B{{F}_{4}}^{-}\) \(N{{H}_{4}}^{+}\) \(Xe{{O}_{4}}\...
The ion which is not tetrahedral in shape
BF4−
NH4+
XeO4
ICl4−
Solution
The 3-D arrangement of atoms in a molecule is known as its molecular geometry. The molecular geometry includes the shape of the molecule as well as the bond length and bond angles of the molecule. All these factors help to determine the position of each atom in the geometry.
Complete step by step solution:
The general formula which we use to calculate the hybridization of a molecule is
Hybridization number =21[V+M−C+A]
Here V = the number of valence electrons of the central atom
C = charge on cation
A= charge on anion
M is the number of atoms linked to the central atom
For BF4−
Hybridization number = 21[3+4−0+1]=4
And hybridization will be sp3 and shape is tetrahedral
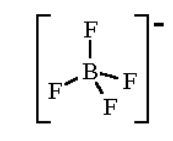
For NH4+
Hybridization number = 21[5+4−1+0]=4
And hybridization will be sp3 and shape is tetrahedral
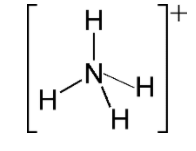
For XeO4
Xe has 8 unpaired electrons but oxygen is not a monovalent atom, oxygen is a divalent atom and the above rule is only applicable for monovalent atoms. Another way to calculate hybridization is adding sigma bonds to lone pairs.
Xe has no lone pair and form 4 sigma bond: hybridization = 4+0=4
And hybridization will be sp3 and shape is tetrahedral
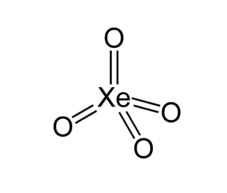
For ICl4−
Hybridization number = 21[7+4−0+1]=6
And hybridization will be sp3d2 and the shape is square planar.
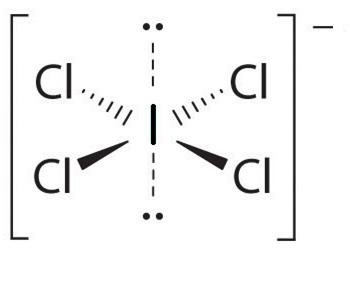
Hence the correct option is option (D)
Note: The geometry and shape of a molecule can be the same or different as the geometry of the molecule depends on the arrangement of lone pair and bond Pair while the shape of a molecule excludes the lone pair on the central atom.
