Question
Question: The involuntary muscle that moves food through the digestive system is called what kind of muscle?...
The involuntary muscle that moves food through the digestive system is called what kind of muscle?
Solution
Muscle is a type of soft tissue that can be found in both animals and people. Muscle cells are made up of actin and myosin protein filaments that slide past one another, causing contraction and changing the length and shape of the cell.
Complete answer:
Unstriped or non-striated muscles are other names for involuntary muscles. The muscles that function or contract without conscious control and are controlled by the autonomic nervous system are known as these muscles.
Smooth muscles are spindle-shaped muscle fibers with a single nucleus in the human muscular system. Smooth muscles have a thickness of 3-10 µm and a length of 20 to 200 µm, which is shorter than skeletal muscle. These muscles produce their connective tissue because they lack filaments, special proteins, actin, and myosin.
Uninucleate, small, spindle-shaped involuntary muscles can be found in the abdominal muscles, cardiac muscles, locomotory muscles, middle ear muscles, and the diaphragm. The contraction of involuntary muscles is slower and more rhythmic than that of voluntary muscles. Involuntary Muscles include Cardiac Muscles, Smooth Muscles, and Skeletal Muscles.
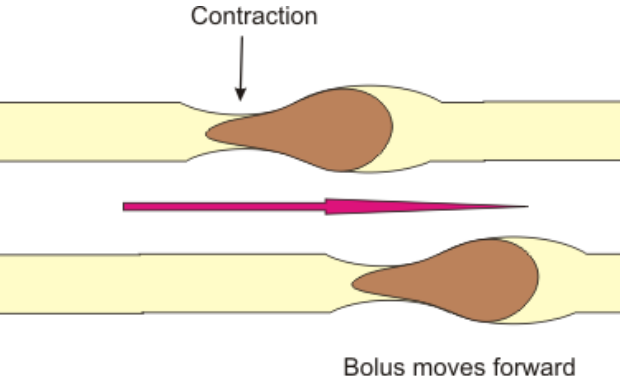
Smooth muscles line the inside of the digestive tract's wall. Peristalsis is a movement that occurs when a muscle contracts and relaxes. Food is propelled through the digestive tract by peristalsis.
The diagram below depicts a cross-section of the intestine (a part of the digestive tract). The smooth muscles in the intestine wall can be seen here. Food is moved through the digestive tract by smooth muscles.
Thus, Peristalsis is a series of muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract in a wave-like pattern.
Note:
The terms single-unit and multi-unit smooth muscle, on the other hand, are oversimplifications. This is because smooth muscles are controlled and influenced by a variety of neural elements for the most part. Furthermore, it has been discovered that most of the time, cell to cell communication and activators/inhibitors are produced locally. Even in multiunit smooth muscle, this results in a somewhat coordinated response.
