Question
Question: The internal sources of Carbon dioxide in CAM plants A. Oxalo-acetic acid B. Malic acid C. RU...
The internal sources of Carbon dioxide in CAM plants
A. Oxalo-acetic acid
B. Malic acid
C. RUBP
D. PEPA
Solution
Certain plants, especially succulents which grow under extremely xeric conditions, fix atmospheric carbon dioxide in the dark. Since the process is first observed in the plants belonging to the family Crasulscea (e.g., Bryophyllum, Kalanchoe, sedum, etc.) it was termed as crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM).
Complete answer: 1. In the dark (during the night) when the stomata are open, the carbon dioxide reacts with phosphoenol pyruvic acid (PEP) to form oxaloacetic acid (OAA) in presence of the enzyme PEP- carboxylase.
Oxaloacetic acid is subsequently converted to malic acid in presence of enzyme malic dehydrogenase. The reaction occurs in the presence of NADH (which is produced by glycolysis). The malic acid, produced in the dark as a result of acidification, is stored in the vacuole.
2. In light (during the day), when the stomata are closed, the malic acid is decarboxylated to produce pyruvic acid and evolve carbon dioxide. This process is termed deacidification.
The pyruvic acid may be oxidized to carbon dioxide by the Krebs cycle or maybe reconverted to phosphoenol pyruvic acid. The carbon dioxide released by deacidification is accepted by ribulose biphosphate and fixed to carbohydrates by the C3 cycle.
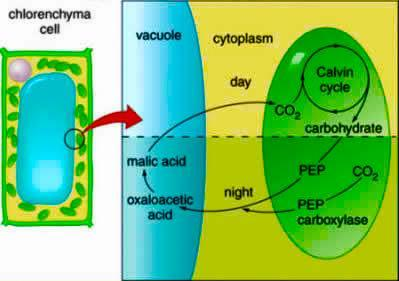
So the correct answer is option A. Oxalo acetic acid.
Note: The metabolic pathway of CAM involves acidification which occurs at night and deacidification which occurs at day time. During the night the organic acid content of CAM plants increases and the pH of their cell sap decreases and the pH of their cell sap increases. Similarly, the storage of carbohydrates increases during the day time and decrease during the night.
