Question
Question: The increasing order of \(\text{ p}{{\text{K}}_{\text{b}}}\text{ }\) of the following compound is: ...
The increasing order of pKb of the following compound is:
| A) | 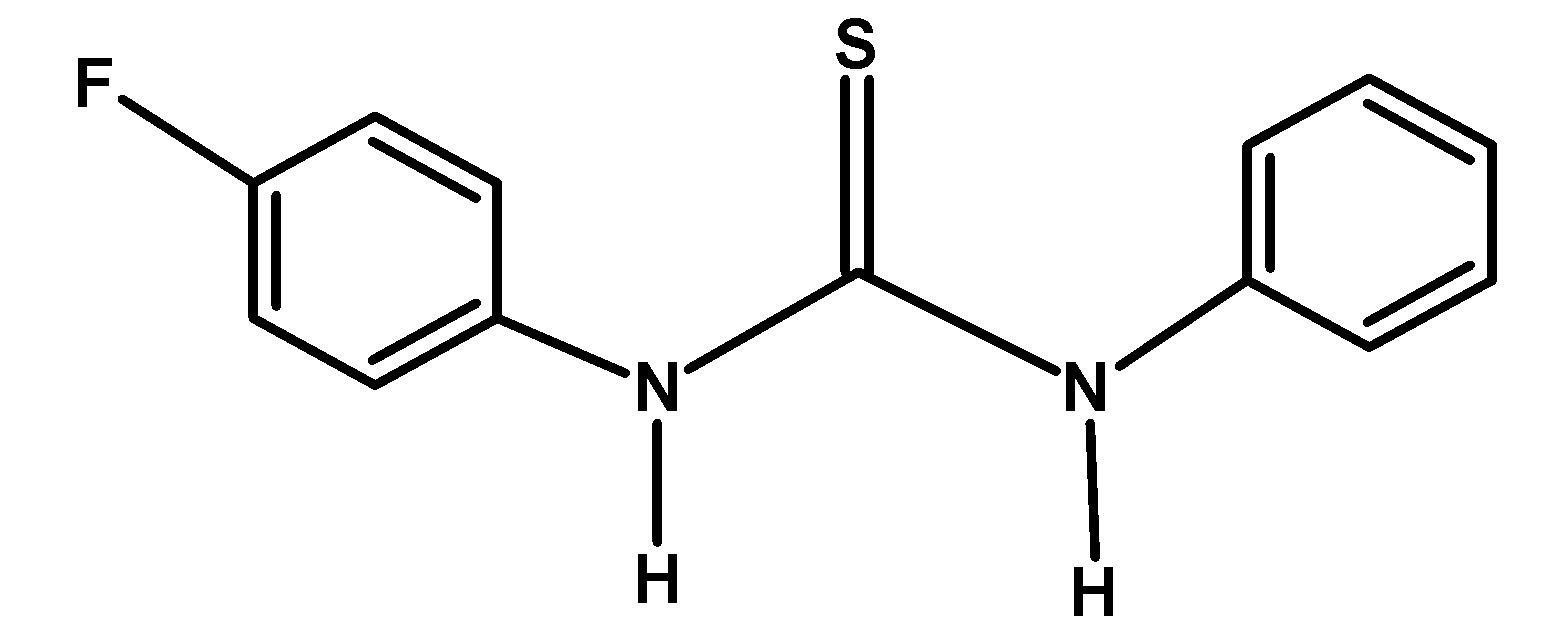 |
|---|---|
| B) | 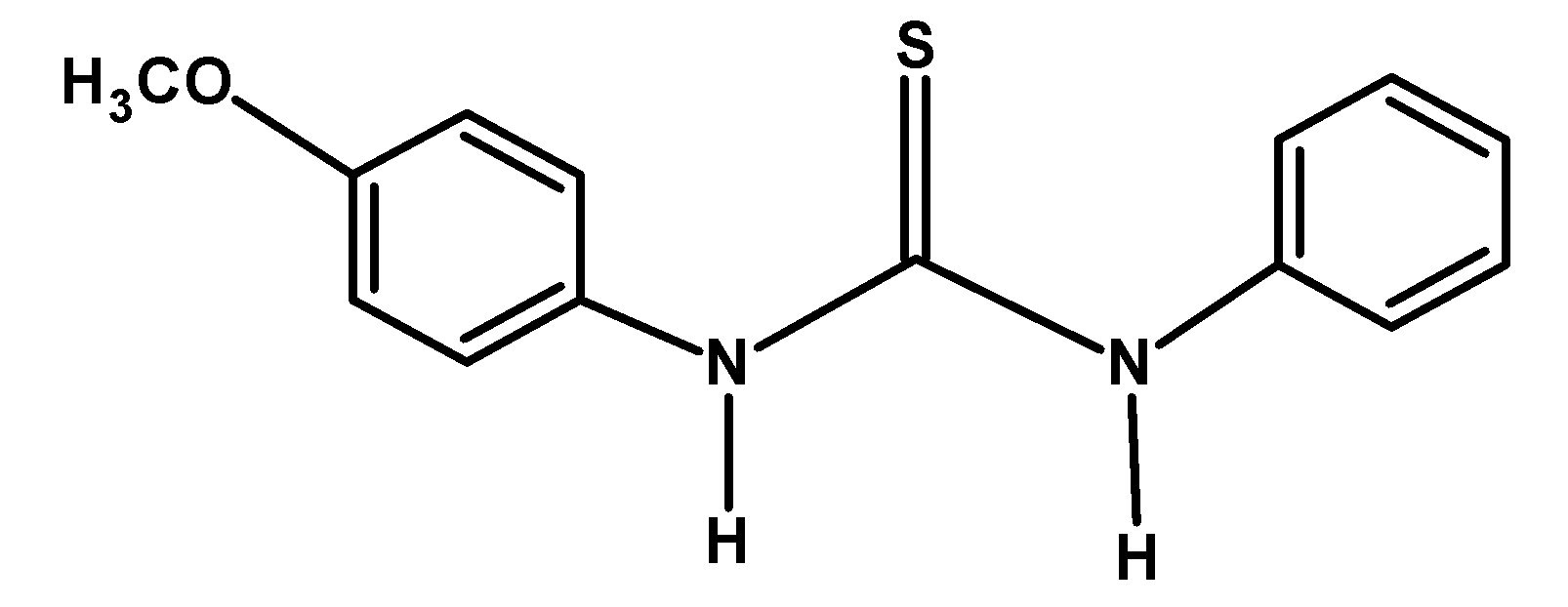 |
| C) | 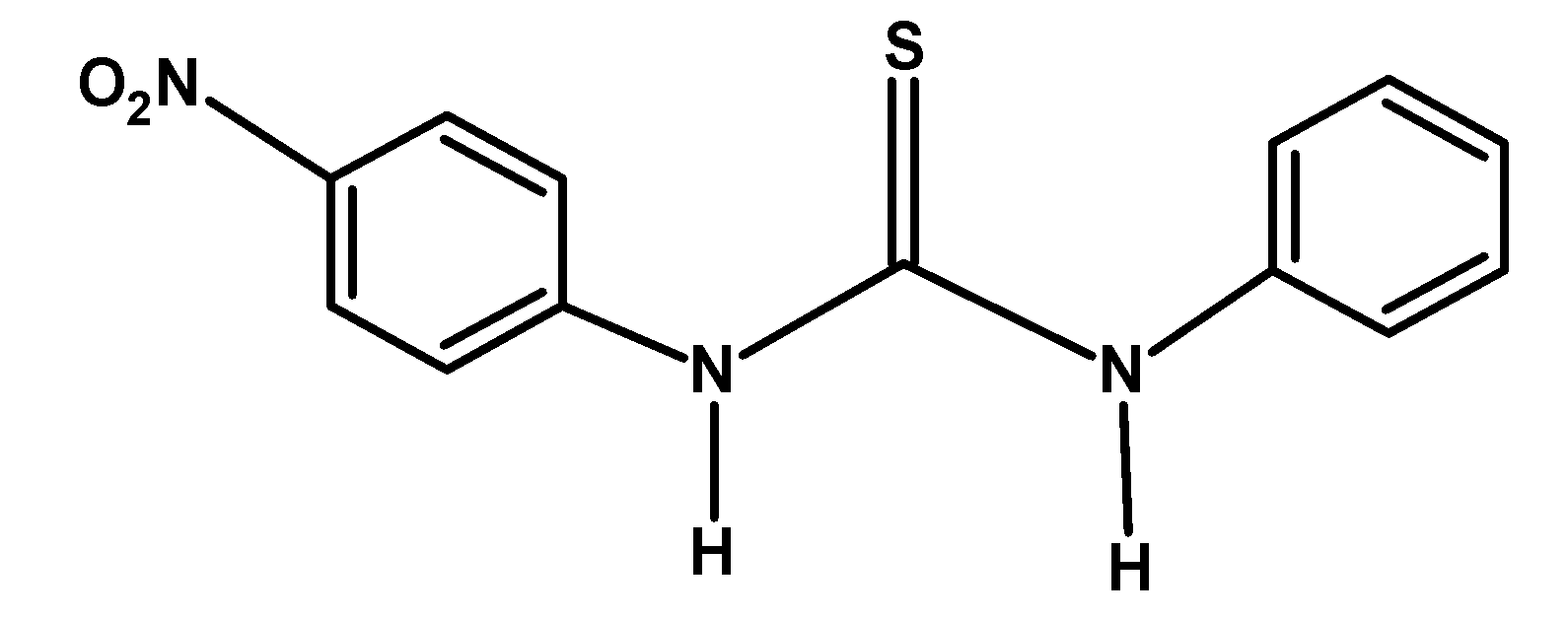 |
| D) | 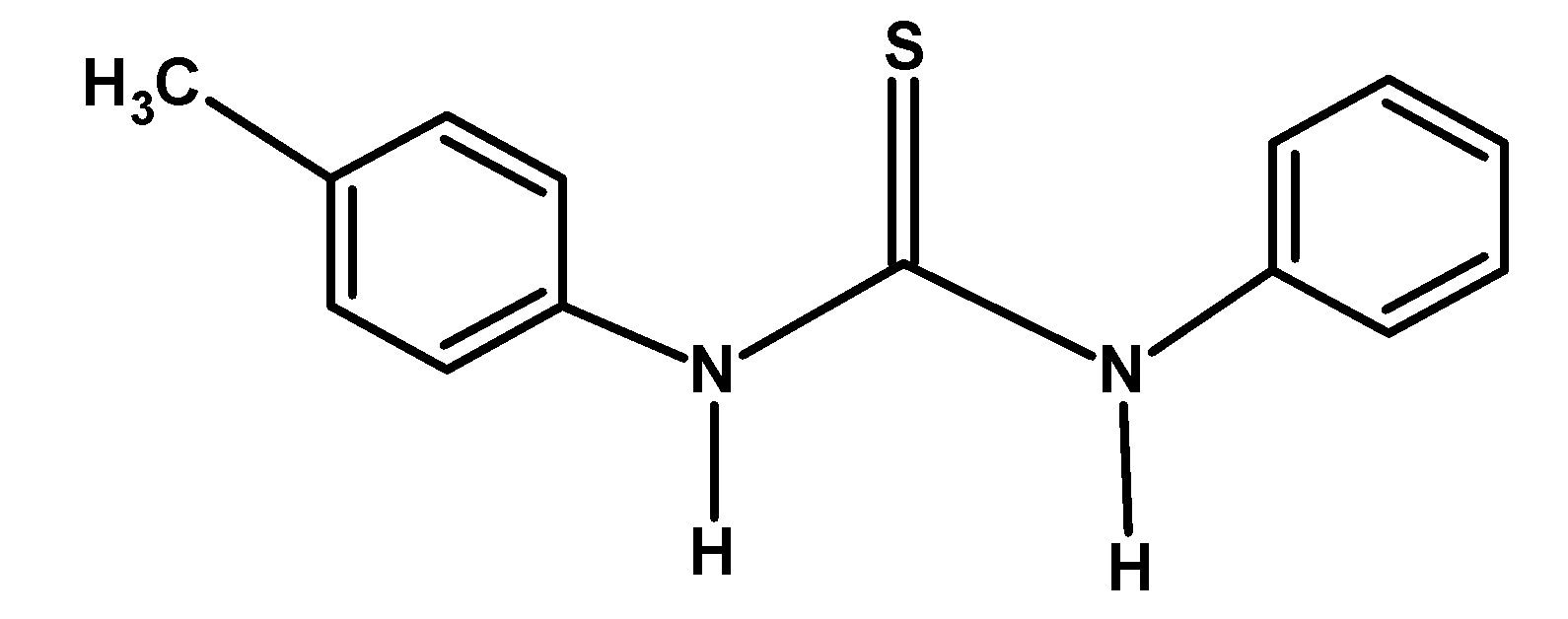 |
A) A < C < D < B
B) B < D < A < C
C) C < A < D < B
D) B < D < C < A
Solution
. The basicity is the measure of the extent of the base to accept the proton or donate the electron pair. The basicity is expressed as a dissociation constant of the base Kb . The basicity of an organic compound depends on the substituents. The electron releasing group increases the basicity of the base while the electron-withdrawing group decreases the basicity of the compound.
Complete step by step answer:
The basicity is determined by the Kb value of a base. the base tends to abstract a proton or donate an electron pair. The value of the Kb is equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the base.
The basicity depends on the substituents present in the compound.
The electron-donating group likes −CH3 and −OCH3 releases the electron density towards the nitrogen of the compound. This stabilized the cation formed after donating an electron pair or accepting a proton. Thus from given compounds, compound B) and D) have high basicity.
Among −CH3 and −OCH3 groups, the methyl group donates its electron via the hyperconjugation and inductive effect. However, the methoxy −OCH3 group donates the electron via the resonance. Thus compound B) has more basicity compared to D).
The electron-withdrawing group like −F and −NO2 withdraws the electron density towards itself from the nitrogen of the compound. This destabilized the cation formed after donating an electron pair or accepting a proton. Thus from given compounds, compound A) and C) have low basicity.
Among −F and −NO2 groups, the Florine group withdraws its electron via the inductive effect. However, the nitro−NO2 group withdraws the electron via the resonance. Thus compound A) has more basicity compared to C).
Thus the order of basicity for the compounds is given as,
B > D > A > C
The Kb is related to pKb is given as,’
pKb = −logKb
Thus, the order of increasing pKb is given as,
B < D < A < C
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Note that, we can summarise the basicity and pKb as basicity is directly proportional to the resonance effect of electron releasing group and hyperconjugation effect of electron-donating group. However, the basicity is inversely related to the resonance effect of the electron-withdrawing group and hyperconjugation effect. Always remember that the resonance effect is the permanent effect but hyperconjugation is a temporary effect, thus resonance makes it more stable.
Basicity ∝ +R ∝ −R1∝ +H ∝ −H1
