Question
Question: The image formed by a convex lens in a microscope is: (A)Virtual and erect (B)Real and inverted ...
The image formed by a convex lens in a microscope is:
(A)Virtual and erect
(B)Real and inverted
(C)Of same size as the object
(D)None of these
Solution
A single convex lens or a group of lenses is used together in order to view objects through a simple microscope. Convex lens or converging lens or Positive lens is used in microscopes to get an enlarged image of the object under study. As the name suggests, mostly microscopic objects are studied under a microscope to view them properly. So the placing of the convex lens is done in such a way as to produce an enlarged image of the object.
Complete answer:
In a simple microscope, the convex lens is placed in such a manner as to obtain an enlarged image. An enlarged and highly magnified image can be formed only when the object is placed in between the focus and the centre of the lens. In other words, if the object distance is less than the focal length of the lens, it gives a highly magnified object. So the placing of the lens is made accordingly.
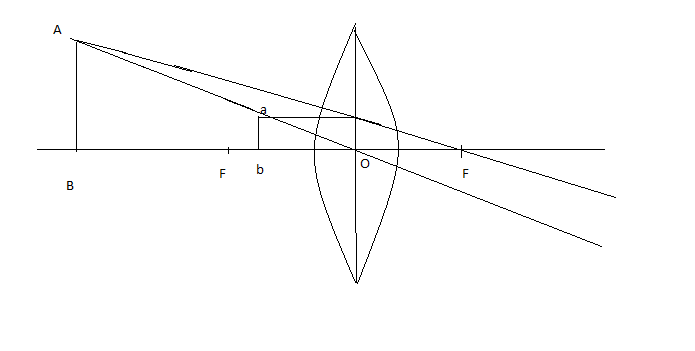
Fig: Ray formation in convex lens
In the figure that shows the ray diagram of such an object, we can see that the image is formed on the same side as that of the object. From this, we can conclude that the image is virtual.
Again, the height of image AB formed is parallel to object ab. So, we can conclude that the image is erect.
The image formed by a convex lens in a microscope is virtual and erect.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
The image formation highly depends on the position of the object in the mirror. A single convex lens or a group of such lenses are used in microscopes to obtain highly magnified objects.
Note:
Alternatively, in place of a ray diagram, the solution of the above problem can be arrived at by using a mathematical method using the Lens formula. Using which we can derive that the image formed in a convex lens when the object is placed between the focus and the centre of the lens (as in the case of a simple microscope) produces a virtual image. The positive sign of magnification further confirms the image is erect.
